Fig. 2.
Mean arterial pressure and short-term survival was attenuated with H2 and XOR-I.
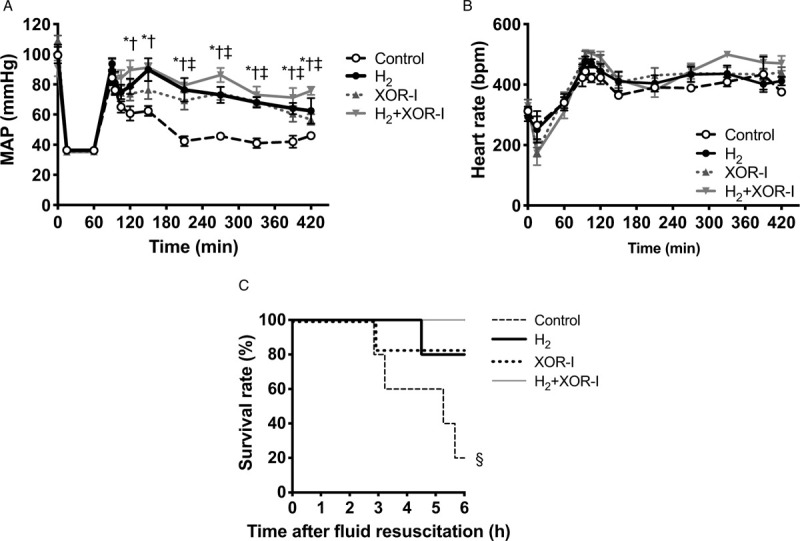
A, MAP was significantly maintained in the H2, XOR-I, and H2+XOR-I groups. With the combination therapy, MAP was maintained at a higher level than either monotherapy. B, Time course changes in heart rate were comparable among the four groups. C, The survival rates 6 h after initiation of fluid resuscitation were 20% (1/5) in the control group, and were 83% (5/6), 80% (4/5), and 100% (5/5) in the XOR-I, H2, and H2+XOR-I treatment groups, respectively. Values are mean ± SEM; n ≥ 5 animals in each group. ∗P < 0.05, H2 compared with the control group; †P < 0.01, H2+XOR-I compared with the control group; ‡P < 0.01, XOR-I compared with the control group; §P = 0.03, compared with the control group. H2 indicates hydrogen gas; MAP, mean arterial pressure; XOR-I, xanthine oxidoreductase inhibitor.
