Figure 1.
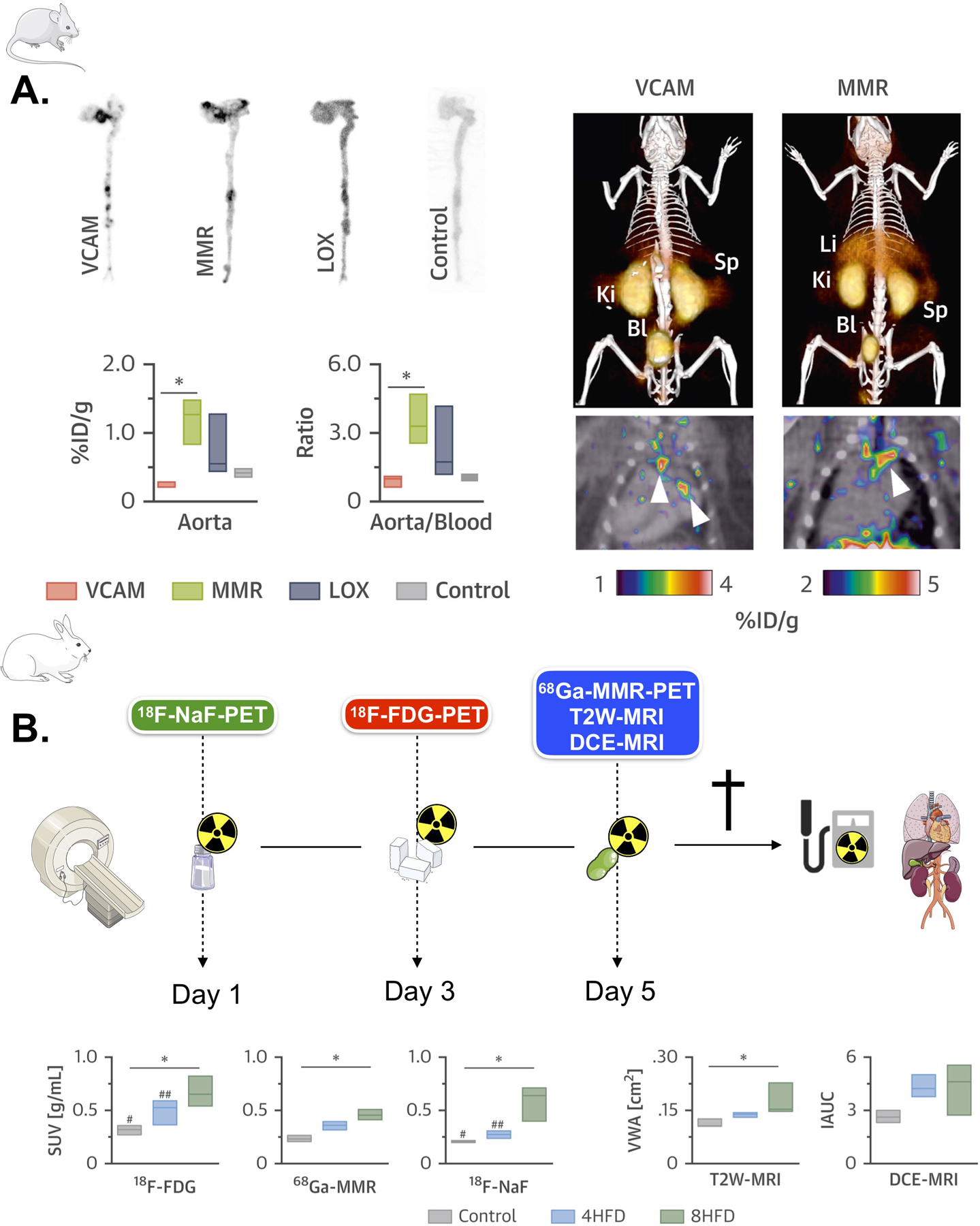
(A) Left, autoradiography and radioactivity concentration in aortas of Apoe–/– mice at 3 h post-injection of the corresponding 64Cu-nanobody (n ≥ 3 per nanobody). Right, representative fused PET/CT images 1 h post-injection of 64Cu-VCAM and 64Cu-MMR in Apoe–/– mice. Arrows indicate enhanced uptake at the aortic arch and root, typical sites of atherosclerotic lesions. (B) Left, rabbit PET/MR imaging schedule. Right, differences in 18F-FDG (3 h p.i.), 68Ga-MMR (2 h p.i.), 18F-NaF (1.5 h p.i.), T2W-MRI and DCE-MRI in healthy and atherosclerotic rabbits (on high-fat diet for 4 months [4HFD] or 8 months [8HFD], n ≥ 3 per group). *p < 0.05. %ID/g = percentage injected dose per gram of tissue; Bl = bladder; Ki = kidney; Li = liver; Sp = spleen; SUV = standardized uptake value. VCAM, vascular cell adhesion molecule. MMR, macrophage mannose receptor. LOX, lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor. 18F-NaF PET, 18F sodium fluoride positron emission tomography. 18F-FDG PET, 18F fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. T2W-MRI, T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging. DCE-MRI, dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. HFD, high fat diet. Adapted from Senders et al29.
