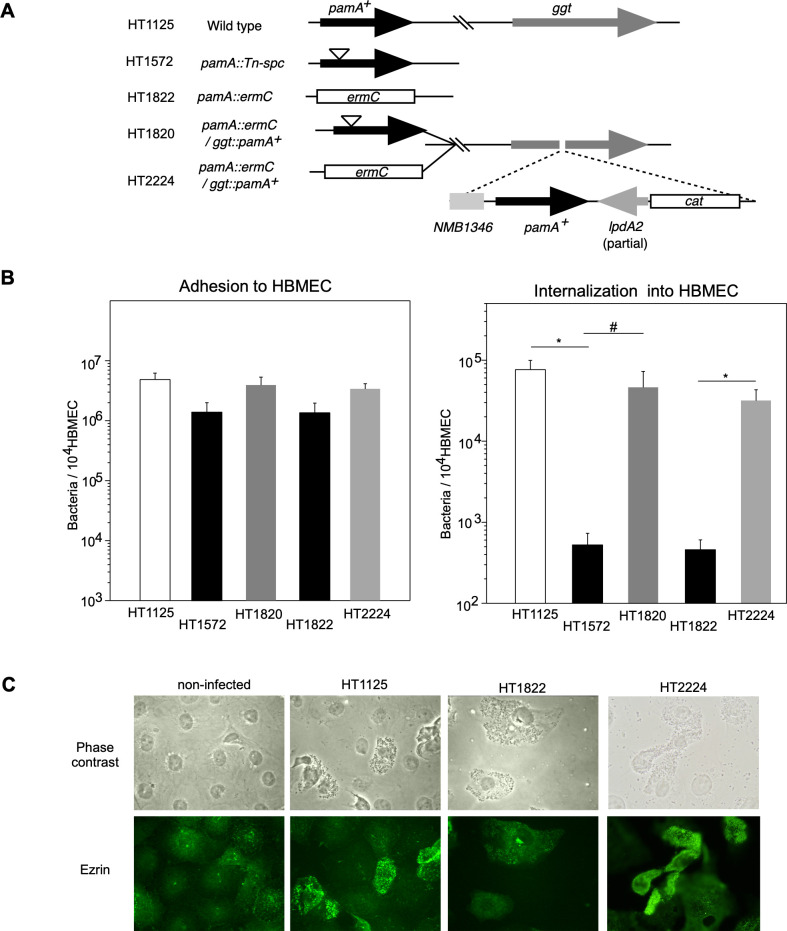
Fig 1. Characterization of ΔpamA N. meningitidis mutant.
(A) Schematic representation of the wild-type, insertion, and deletion mutants in the pamA gene and ectopic complementation of the pamA+ gene at the ggt locus in N. meningitidis strains. (B) Effect of ΔpamA mutation on N. meningitidis infection of HBMEC. The adherence (left) and internalization (right) of pamA N. meningitidis mutants to HBMEC, and the effects of complementation of the pamA+ gene in the pamA deletion mutant on bacterial infection. Each value is the mean ± standard error of the mean (CFU per 104 HBMEC) from at least four experiments. Open, filled, light gray, and dark gray bars indicate the bacterial number of N. meningitidis wild-type pamA+ (HT1125), pamA::Tn-spc (HT1572), and ΔpamA::spc (HT1822), and pamA- mutants in which the pamA+ gene was ectopically complemented (HT1736 and HT2224), respectively (see S1 Table). *P<0.01, #P<0.05, significantly different from the pamA+ strain or pamA- mutants complemented with the pamA+ gene. (C) Immunofluorescence microscopy showing the accumulation of ezrin beneath N. meningitidis-infected HBMEC. The HBMEC monolayer was infected with wild-type pamA+ (middle-left), ΔpamA (middle-right), and ΔpamA/pamA+ (right) N. meningitidis strains. A non-infected HBMEC monolayer is also shown in the left panels. Bacteria and HBMEC were observed by phase-contrast microscopy (upper panels). Ezrin was immunostained with an anti-ezrin mAb and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated rabbit anti-mouse IgG (green channel, lower panels).