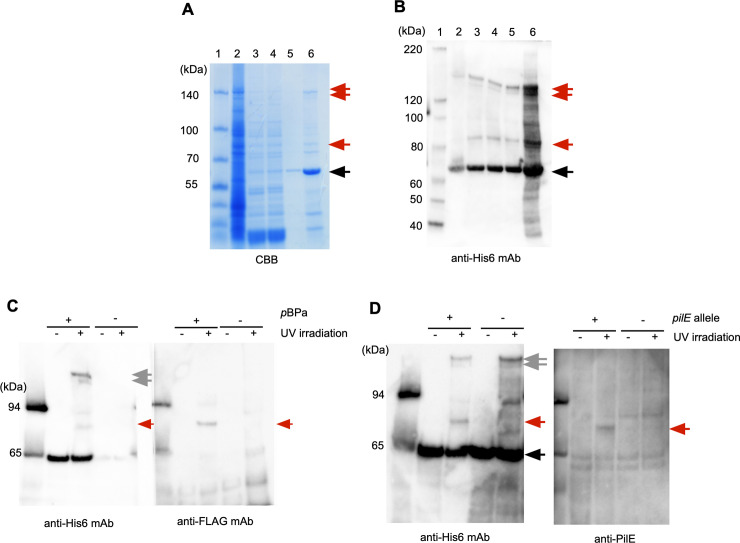
Fig 5. Purification and identification of an endogenous protein crosslinked to PamA K278(pBPa)-Strep2-His6.
Proteins in each purification step were analyzed by 4–12% SDS-PAGE and staining with the CBB staining kit (A) and Western blotting with anti-His6 mAb (B). Lane 1, molecular mass standards; lane 2, N. meningitidis crude soluble extract; lane 3, after the Ni-Sepharose column; lane 4, after dialysis with IP Lysis buffer; lane 5, after the Strep-Tactin Sepharose column; lane 6, after concentration with VIVASPIN TURBO 15. Black and red arrows indicate K278(pBPa)-Strep2-His6 and the unidentified endogenous proteins crosslinked to PamA K278(pBPa)-Strep2-His6, respectively. (C) The PilE-FLAG protein was crosslinked to PamA K278(pBPa) in N. meningitidis. The black arrow shows the full-length PamA K278amb protein expressed by pyrrolysine-based amber suppression with pBPa, and the gray arrow indicates the homotrimer (See text) in N. meningitidis. The red arrow shows the complex of PilE-FLAG crosslinked to PamA K278(pBPa)-Strep2-His6 in N. meningitidis. +/- indicates the presence or absence of pBPa, and irradiation or no irradiation with UV light, respectively. (D) The crosslinked band was reacted with anti-PilE rabbit serum. Black and gray arrows show PamA K278(pBPa)-Strep2-His6 and the putative homotrimer complex of PamA K278(pBPa), respectively, in N. meningitidis. The red arrow shows the complex of PilE crosslinked with PamA K278(pBPa)-Strep2-His6 in N. meningitidis. +/- indicates the presence or absence of the pilE gene, and irradiation or no irradiation with UV light, respectively.