Figure 4.
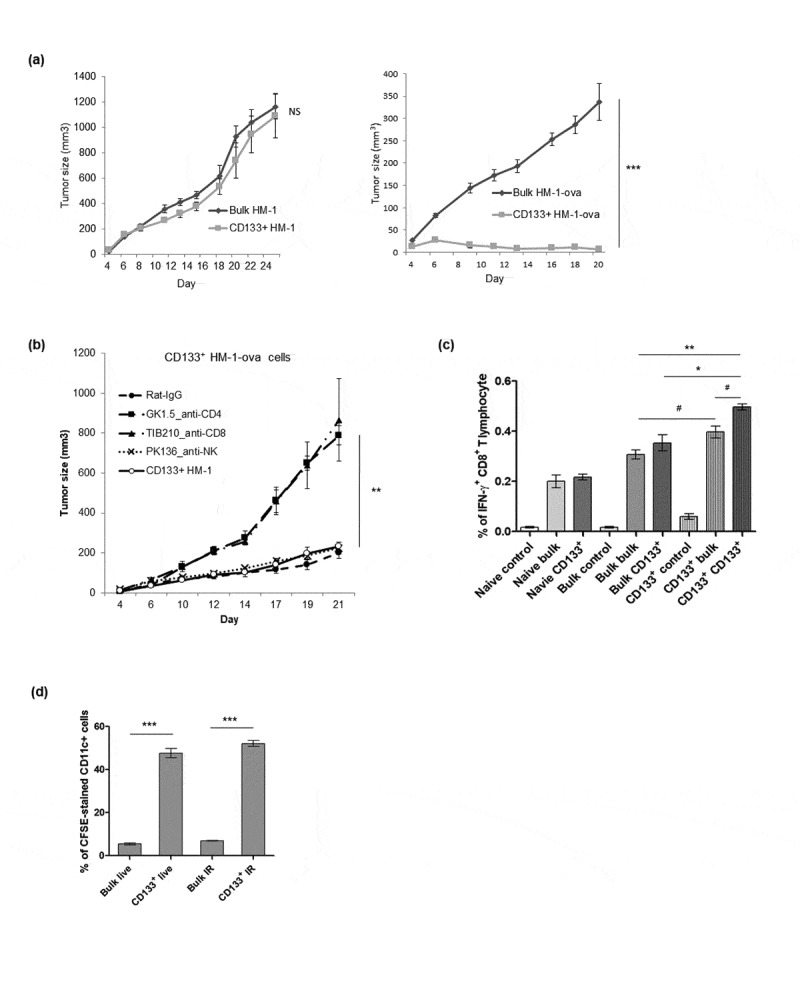
Enhanced immunogenicity of cancer stem-like cells CD133+ HM-1 cells. (a) Tumor growth curve of bulk and CD133+ HM-1 cells showed similar growth pattern (left). However, CD133+ HM-1 cells expressing chicken ovalbumin (CD133+ HM-1-ova) were rejected. Bulk HM-1 cells expressing ovalbumin grew slowly but could still form the tumors (p < .0001, right). (b) Suppression of CD133+ HM-1-ova tumor growth was abolished through depleting CD8+ and CD4+ T lymphocytes by TIB210 (anti-CD8) and GK1.5 (anti-CD4) neutralizing antibodies (p < .001), suggesting rejection of CD133+ HM-1-ova tumor involved CD8+ and CD4+ T cell immune response. (c) Mice were either not immunized (naïve), immunized with bulk HM-1 or CD133+ HM-1 cells. The re-stimulated antigens were either nothing (control), bulk or CD133+ HM-1 cells. Splenocytes from mice immunized with CD133+ HM-1 cells are associated with more CD8+ IFN-γ+ T lymphocyte by the same stimulating cells (p < .001, Bulk bulk vs CD133+ CD133+; p < .05, Bulk bulk vs CD133+ bulk, the former is cells for immunization, the latter is cells for re-stimulation in assay). Vaccination with bulk cells induced less activated CD8+ T lymphocytes. (d) CFSE-pulsed bulk and CD133+ HM-1 cells were incubated with syngeneic CD11c+ cells for 6 hours. Phagocytosis was analyzed by flow cytometry for CFSE-stained CD11c+ cells. Increased phagocytosis of CD11c+ cells was observed on both live and irradiated CD133+ HM-1 cells (p < .0001 on both). #p < .05, *p < .01, **p < .001, ***p < .0001, NS: not significant.
