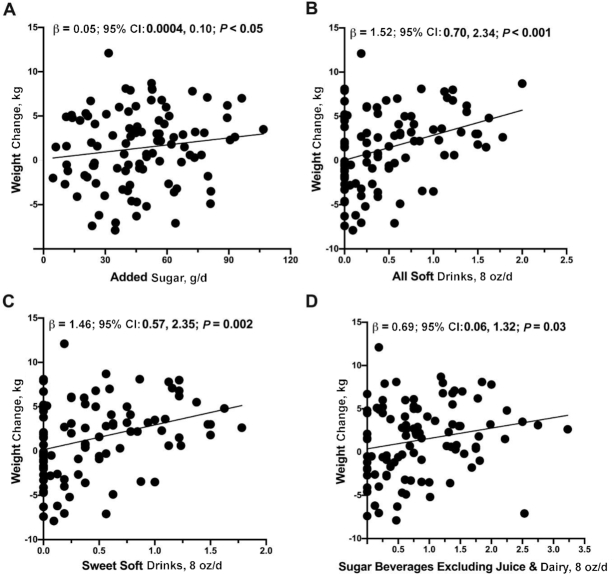
FIGURE 1.
Added sugar and servings of sugary beverages were associated with increased maternal weight from 1 to 6 mo postpartum. Servings of (A) added sugar (g/d), (B) all soft drinks (8-oz servings/d), (C) sweet soft drinks (8-oz servings/d), and (D) sugary beverages excluding juice and dairy (8-oz servings/d) were positively associated with maternal weight change in 99 women. Dietary factors are shown for grams or 8-oz (equivalent to 236.6 mL) servings per day. Unadjusted values for change in maternal weight from 1 to 6 mo compared with servings of soft drinks are shown. Multiple linear regression was performed to obtain the effect sizes (β) and 95% CIs after adjustment for mothers’ baseline age, height, and total energy intake (kcal). Plots show beverage servings in 8 oz/d and effect estimates (β) are reported for a half serving per day difference in beverage consumption.