Figure 1.
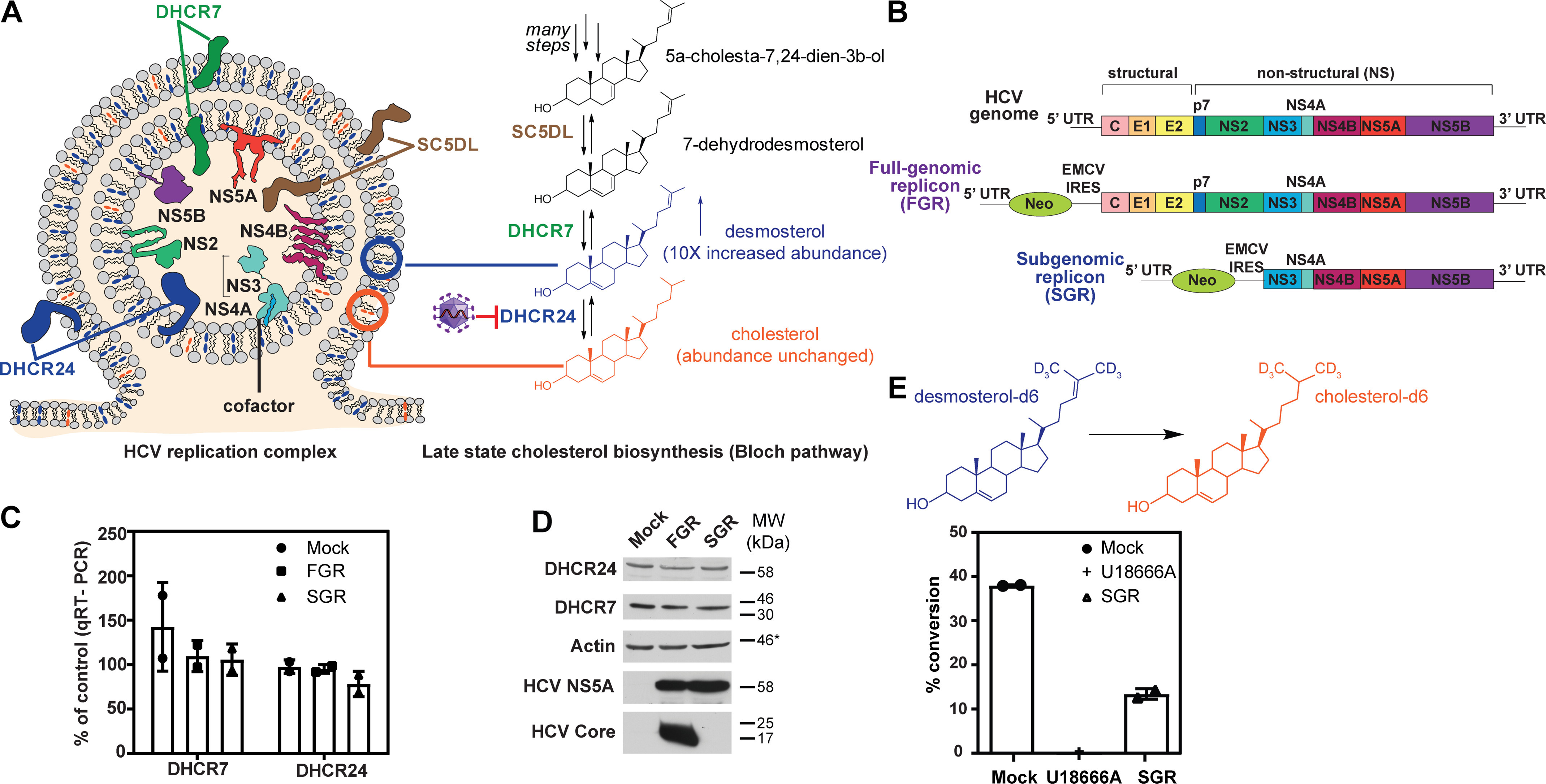
Effect of HCV on enzymes in the Bloch pathway of late-stage cholesterol biosynthesis. A, the nonstructural (NS) proteins of HCV form a replication complex located on a specialized membrane derived from the host ER. Our data indicate that the enzymes that catalyze cholesterol biosynthesis, which are integral membrane proteins found on the ER surface, co-reside with the nonstructural proteins on the replication membrane in addition to being present on ER membrane itself. Desmosterol, the penultimate molecule in the Bloch branch of cholesterol biosynthesis, is depicted as blue ovals; cholesterol is depicted as orange ovals. B, FGR and SGR RNAs derived from HCV clone JFH1 were used as experimental models to examine the effects of HCV on desmosterol synthesis and metabolism. Replicons were stably expressed in Huh7.5 cells. C, FGR and SGR RNAs do not significantly alter mRNA abundance of DHCR7 or DHCR24, as measured by RT-qPCR. The bar graph represents the average of two biological replicates with error bars equal to the standard deviation. Neither FGR nor SGR caused a significant change in the abundance of DHCR7 or DHCR24 transcripts. D, the SGR RNA does not cause a significant change in the steady-state abundance of DHCR7 or DHCR24 proteins as assessed by immunoblot of whole-cell lysates. *, The molecular mass (MW) marker for the immunoblot probed for actin was excised during processing; however, the actin band relative to core and NS5A was consistent between this and other immunoblots in which the molecular mass markers were recorded. The location of the 46-kDa marker relative to actin on comparable immunoblots is indicated. E, cellular conversion of deuterated desmosterol (desmosterol-d6) to deuterated cholesterol (cholesterol-d6) was monitored by extraction of cellular lipids and quantification of desmosterol-d6 and cholesterol-d6 by LC-MS. No conversion of desmosterol-d6 to cholesterol-d6 was observed in cells treated with U18666A, a DHCR24 inhibitor, which was used as a positive control. The presence of the SGR RNA causes a significant decrease in conversion of desmosterol-d6 to cholesterol-d6 (Student's t test p value of 0.0012 when compared with Huh7.5-negative control cells, “Mock”). The bar graph represents the average of two biological replicates with error bars equal to standard deviation.
