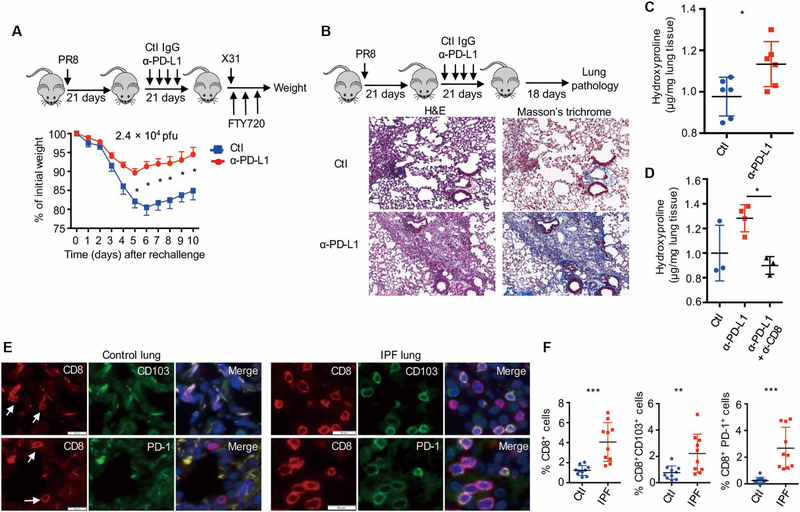
Fig. 7. TRM cell exhaustion balances protective immunity and fibrotic sequelae.
(A) WT mice were infected with influenza PR8 and received control IgG (Ctl) or α-PD-L1 from 21 to 37 d.p.i. Mice were rechallenged with influenza X31 (2.4 × 104 pfu) in the presence of FTY720 at 42 d.p.i. Percentages of original weight were determined daily after rechallenge. (B to D) WT mice were infected with influenza PR8 and received control IgG (Ctl) or α-PD-L1 from 21 to 37 d.p.i. Lung pathology and hydroxyproline levels were determined at 60 d.p.i. (B) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Masson’s trichrome C staining of lung sections. (C) Hydroxyproline levels (micrograms per milligram of lung tissue) of the lungs. (D) Hydroxyproline levels of the lungs from mice received control Ab, α-PD-L1, or α-PD-L1 plus α-CD8 (CD8 depletion). (E and F) CD8, PD-1, and CD103 staining was performed on lung sections from control (n = 10) or patients with IPF (n = 10). (E) Representative of CD8, PD-1, and CD103 staining. Blue, DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole). (F) Frequencies of CD8+ cells, CD8+ CD103+, or CD8+ PD-1+ cells in DAPI+ cells of control or IPF lungs. (A to D) Representative of two to five experiments (n = 3 to 6). Mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, unpaired two-tailed t test.