Fig. 7. ABHD4 is necessary for cell death caused by fetal alcohol exposure.
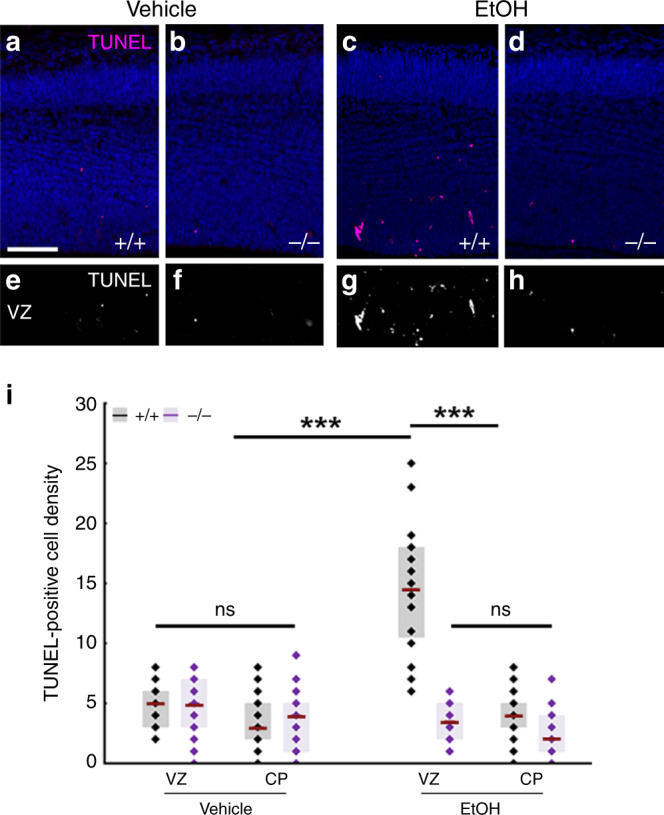
Compared to vehicle-treated mice (a, b, e, f), increased number of TUNEL-positive dead cells is seen in ethanol-treated wild-type (+/+), (c, g), but not in Abhd4-knockout (−/−) mice (d, h) in the ventricular (VZ) zones of embryos derived from dams undergoing subchronic alcohol treatment, but not in the cortical plate (CP). i Quantification of the density of TUNEL-positive cells in the VZ and in the CP after subchronic ethanol-treatment (Kruskal–Wallis test with post hoc Dunn’s test, ***P < 0.0001; ns = not significant, P ≈ 1, n = 31 sections from n = 5 animals per wild-type, vehicle-treated mice, n = 27 sections from n = 4 animals per Abhd4-knockout, vehicle-treated mice, n = 24 sections from n = 4 animals per wild-type, ethanol-treated mice, n = 18 sections from n = 3 animals per Abhd4-knockout, ethanol-treated mice). Graphs show box-and-whisker plots (including minima, maxima, and median values, lower and upper quartiles) with single values. Scale bars: a–h: 100 μm. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
