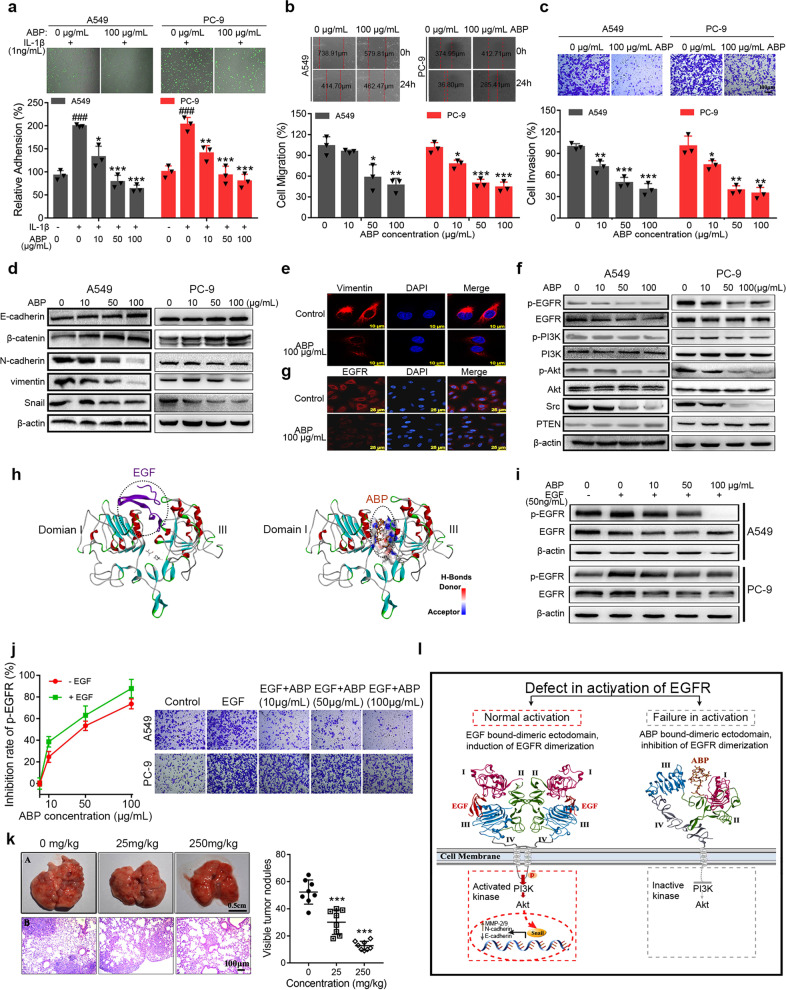
Fig. 1.
ABP inhibits cell adhesion, migration, and invasion through targeting EGFR. a Effect of ABP on adhesion of A549 and PC-9 cells to HPMECs. Upper panel: representative fluorescence microscopic images showed that ABP inhibited the adhesion of rhodamine-123 labeled A549 and PC-9 cells to the HPMECs monolayers stimulated by IL-1β (1 ng/mL). Lower panel: quantitative analyses of the inhibition of ABP on the adhesion of A549 and PC-9 cells to HPMECs. ###P < 0.001 compared to the control group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared to IL-1β-treated group. b, c Effect of ABP on migration (b) and invasion (c) of A549 and PC-9 cells. Upper panel: representative micrographs of A549 and PC-9 cells. Lower panel: quantitative analyses of the effect of ABP on cell migration or invasion. The data represented mean ± SD, n = 3; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared to the control group. d Western blot analyses of E-cadherin, β-catenin, N-cadherin, vimentin, and Snail protein expressions in A549 and PC-9 cells treated with ABP for 24 h. e Double immunofluorescence staining with DAPI and anti-vimentin antibody was carried out for A549 cells treated with ABP for 24 h. f Western blot analyses of EGFR, p-EGFR, PI3K, p-PI3K, Akt, p-Akt, Src, and PTEN expression levels in A549 and PC-9 cells treated with ABP for 24 h. g Double immunofluorescence staining with DAPI and anti-EGFR antibody was carried out for A549 cells treated with ABP for 24 h. h Comparison of computational predicted binding site of ABP and EGF with EGFR. Minimized Affinity: −9.08. Positions of the binding sites are outlined in dotted circles. i After treatment with ABP (10, 50, 100 μg/mL) for 24 h, cells were exposed to 50 ng/mL EGF for 10 min. Western blot analysis the effect of ABP on protein expressions of p-EGFR and EGFR. j Left panel: inhibition profiling was tested at the indicated concentrations of ABP with or without exposure to EGF in A549 cells. Right panel: The invasion ability of A549 and PC-9 cells in untreated, EGF (20 ng/mL) treated, and EGF (20 ng/mL) plus indicated concentrations of ABP-treated groups was assessed by transwell analyses. k Left panel: A, Photography of lungs of the mice inoculated with LLC cells via hypodermic injection; B, HE staining of lung metastatic nodules, amplification ×10. Right panel: the number of tumor metastatic nodules in the lungs of the mice. Data represented the mean ± SD, n = 8; ***P < 0.001 compared to the control group. l The possible mechanisms by which ABP inhibits cancer metastasis. ABP binding to extracellular domain of EGFR inhibits its activation and downstream signaling pathways, and blocks EMT process including inhibition of Snail expression, downregulation of N-cadherin and matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 (MMP-2/9), and upregulation of E-cadherin. EGF or ABP interacts with sites in domain I and domain III of EGFR. Domain II is dimerization arm, which extends the dimerization arm to hold the body of the other. In the left panel, the EGF chains in the EGF•EGFR dimer (pdb id 1mox) complex are red. Domains I, II, III, and IV in the receptor in the dimer are colored dark purple, green, blue, and gray, respectively. In the right panel, ABP in the ABP•EGFR complex is dark orange and domains I, II, III, and IV are colored dark purple, green, blue, and gray, respectively. The active kinases and downstream molecules are in red dotted square box; the inactive kinases in right panel are in gray dotted square box