Figure 4. AC40 recruits IN1 at the RDN1 repeats.
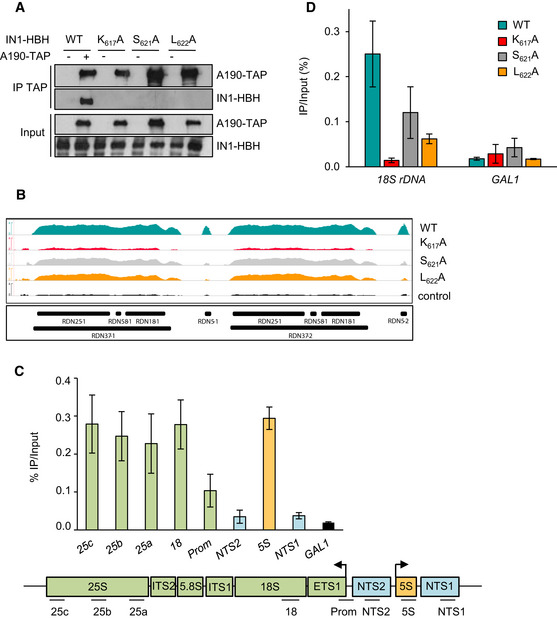
- Co‐immunoprecipitation of ectopic IN1 using TAP‐tagged‐A190 as bait from yeast protein extracts expressing WT or the indicated IN1‐HBH mutants from a pTet‐Off promoter in the absence of doxycycline. Expected sizes are 204 kDa for A190‐HA and 82 kDa for IN1‐Strep (WT and mutants).
- Genome browser visualization of HA‐IN1 occupancy at the RDN1 locus. Occupancy of WT HA‐IN1 and K617A, S621A, and L622A HA‐IN1 mutants is represented in each panel. Control, as described for panel 3D.
- Top. IN1 is recruited at Pol I‐transcribed genes. ChIP‐qPCR analysis as described for panel 3B. Data represent means ± SD (n = 3). Bottom. Schematic representation of the RDN1 locus with DNA amplicon positions.
- Recruitment of WT and mutant HA‐IN1 (K617A, S621A, or L622A) at the 18S rDNA locus transcribed by Pol I. ChIP‐qPCR analysis as described for panel 3B. Data represent means ± SD (n = 3). GAL1 ORF serves as a control.
Source data are available online for this figure.
