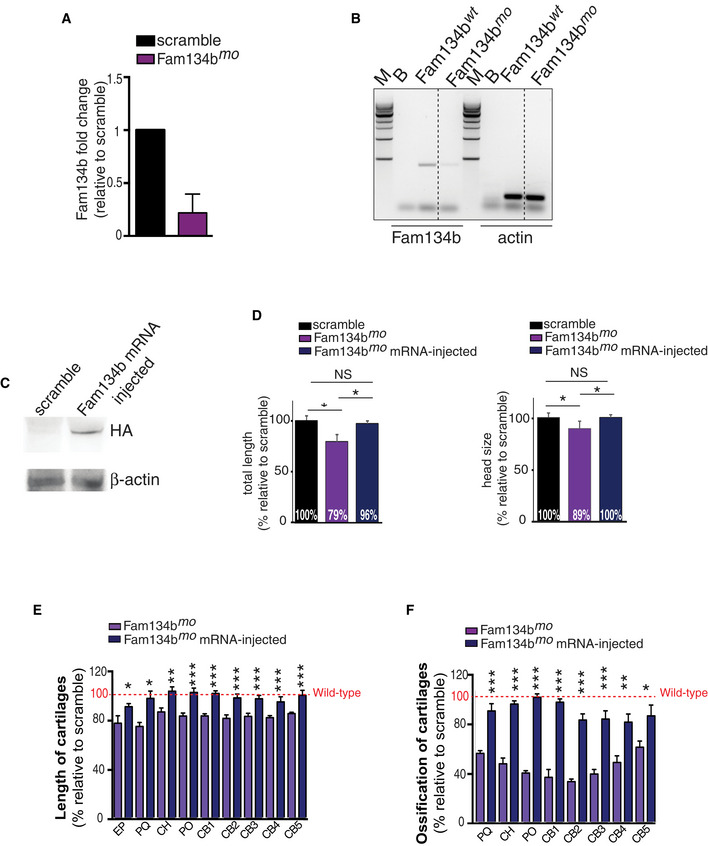
Figure EV5. Fam134b‐HA mRNA expression rescued Fam134b mo skeletal phenotype.
-
AqRT–PCR analysis of Fam134b gene in medaka fish with indicated genotypes. Values were normalized to Hprt gene and expressed as fold change relative to scramble fish. Mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of N = 3 biological replicates.
-
BReverse transcription–PCR analysis of Fam134b gene in Fam134b wt and Fam134b mo medaka fish. Actin gene was used as control gene. M = marker; B = blank.
-
CWestern blot analysis of HA‐tag from a pool of medaka fish embryos injected with scramble or injected with mRNA produced from human HA‐FAM134B pcdna3.1(+). β‐actin was used as a loading control.
-
DBar graphs show quantification of total length and head size of medaka fish model of Fam134b mo and mRNA‐injected Fam134b mo expressed as % relative to the scramble. Mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of at least n = 8 fish per genotype. Student's unpaired t‐test *P < 0.05; NS, not significant.
-
E, FBar graphs show quantification of Alcian Blue (cartilage) (e) and Alizarin Red (bone) (f) staining of Fam134b mo and mRNA‐injected Fam134b mo. Ethmoid plate (EP), palatoquadrate (PQ), ceratohyal (CH), paired prootics (PO), ceretobranchials 1–5 (CB1 to CB5) cartilage length (E), and bone mineralization (F) were evaluated. Values were expressed as % relative to the scramble (100% red dotted line). Mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of at least n = 6 fish/genotype. Student's unpaired t‐test *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.0005 for comparison between Fam134b mo and mRNA‐injected Fam134b mo medaka.
Source data are available online for this figure.
