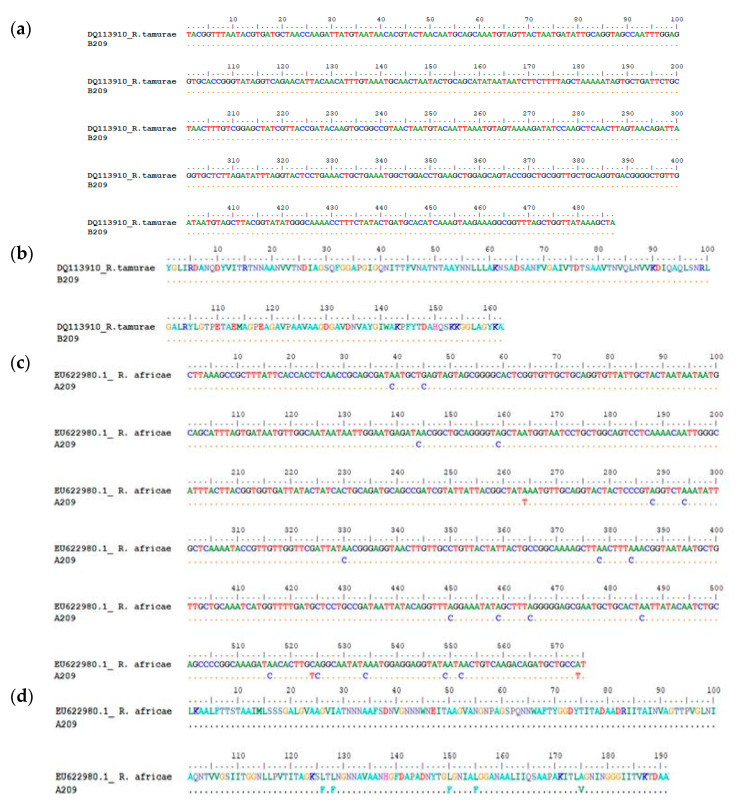
Figure 3.
(a) Nucleotide sequence alignment of the ompB gene of sample B209 against the homologous reference sequence of R. tamurae (DQ113910) indicating 100% homology. Reference sequence was obtained based on highest percentage homology that the test sequence has with R. tamurae which was obtained through Nucleotide BLAST tool in the GenBank. The dots represent nucleotide similarity of the query sequence with the reference strain. (b) Amino acid sequence alignment of the ompB gene of sample B209 against the homologous reference sequence of R. tamurae (DQ113910) indicating 100% homology. Reference sequence was obtained based on highest percentage homology that the test sequence has with R. tamurae which was obtained through Nucleotide BLAST tool in the GenBank. The dots represent amino acid similarity of the query sequence with the reference strain. (c) The degree of homology between test sequence A209 and R. africae (EU622980.1) reference strain: Nucleotide sequence alignment of the ompA gene of sample A209 against the homologous reference sequence of R. africae (EU622980) indicating high homology with R. africae whereas the ompB gene of the same sample has 100% identity with R. tamurae. The dots represent nucleotide similarity of the query sequence with the reference strain. (d) Amino acid sequence alignment of the ompA gene of sample A209 against the homologous reference sequence of R. africae (EU622980). The dots represent amino acid similarity of the query sequence with the reference strain.