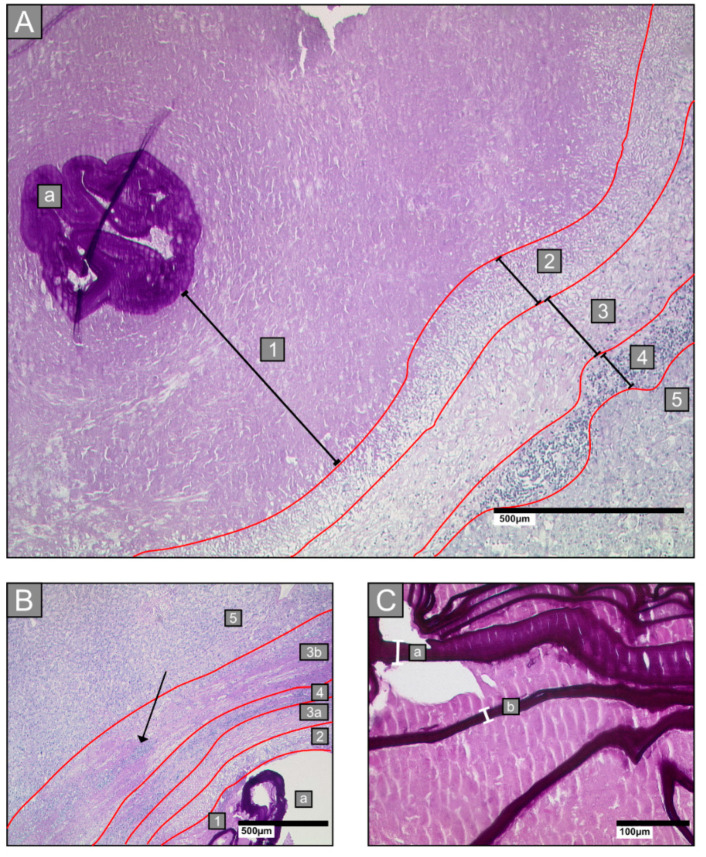
Figure 1.
Examples of histological analyses of liver alveolar echinococcosis infections. Sections were stained with Periodic acid–Schiff. (A): Infections by Echinococcus multilocularis larvae are characterised by five zones: zone 1: necrotic area, surrounding the laminated layer (a); zone 2: inner layer of epithelioid cells and granulocytes; zone 3: fibrotic area; zone 4: outer layer of lymphocytes; zone 5: adjacent liver tissue. (B): An example of zone 3b, which is particularly apparent in Echinococcus multilocularis Ulm Classification for Computed Tomography (EMUC-CT) type III lesions. This zone comprises an additional fibrotic rim between zone 4 and zone 5. Lymphocyte infiltrates can also be found in zone 3b (arrow) (a: laminated layer; 1: necrotic zone; 2–4: border zone; 5: liver host tissue; 3b: outer fibrotic rim). (C): Examples of laminated layer width measurements (indicated with white brackets labelled a and b) in Periodic Schiff staining (PAS)-stained tissue (a = 26.7 µm; b = 14.1 µm).