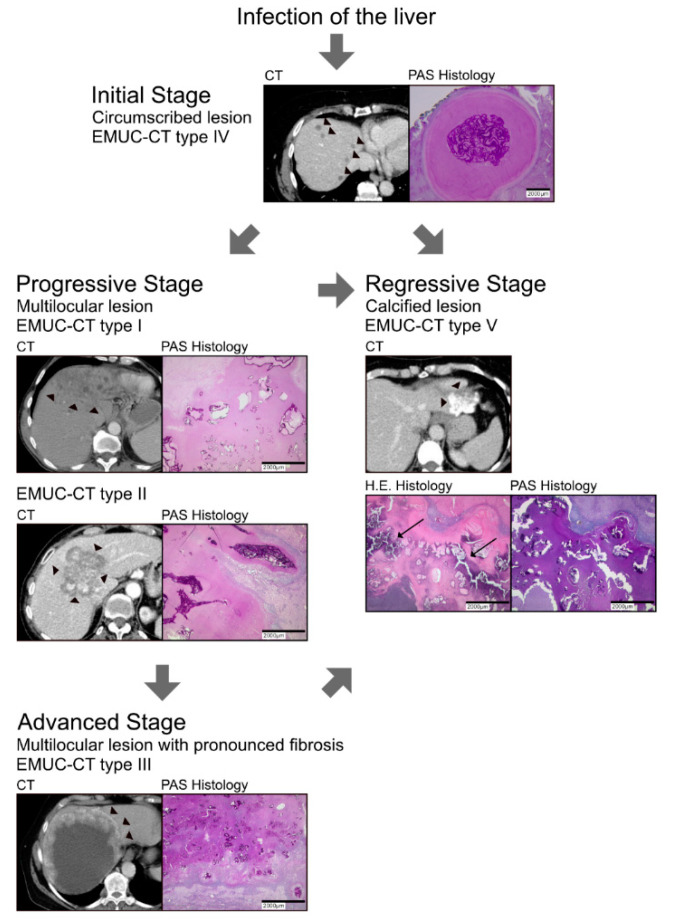
Figure 4.
Proposed model of the evolution of alveolar echinococcosis infections in the liver. (Top) The initial stage (EMUC-CT type IV) is characterised by a small, well-circumscribed lesion (left, arrowheads show multiple small lesions) with few laminated layers (right, intense PAS stain). (2nd row) A lesion in the initial stage can progress in two ways: (left) it can develop to the progressive stage (CT types I and II) when the laminated layer spreads out (arrowheads show the edge of the lesion); alternatively (right), it can eventually become calcified (arrows in HE histology) and regress (regressive stage, CT type V). (3rd row) The progressive stages can evolve to an advanced stage (CT type III; arrowheads show the edges of the lesion).