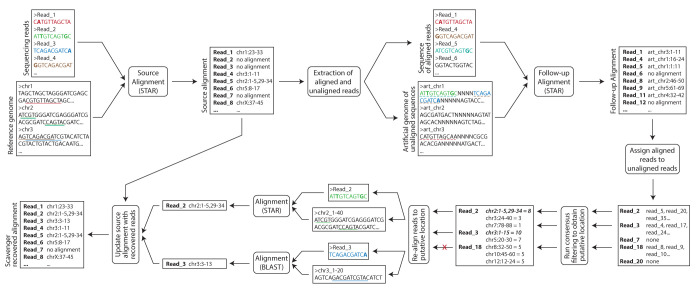
Figure 1. Overview of the Scavenger pipeline.
Scavenger first aligns sequencing reads against the reference genome using the STAR alignment tool in the source execution step. Scavenger then extracts both the aligned and unaligned reads from the source alignment result and creates a sequencing reads file based on the aligned reads and an artificial genome file containing chromosomes built using sequences of unaligned reads. The sequences of aligned reads are then aligned to the artificial genomes using the same alignment tool from the source execution (STAR) in the follow-up execution steps to find aligned reads which have similar sequences to unaligned reads. Next, consensus filtering is performed to select putative sites for re-aligment based on where the majority of aligned reads originate from in the reference genome. Finally, re-alignment is performed for unaligned reads which pass consensus filtering and the source alignment result is updated based on the result of re-alignment.