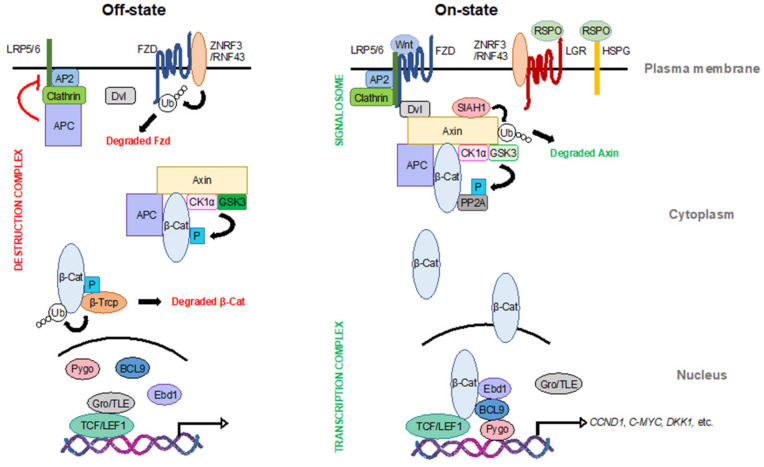
Figure 1.
The canonical Wnt signaling pathway. In the Wnt off-state (left), β-catenin, the pivotal transcription coactivator of the Wnt pathway, is degraded by the destruction complex in the cytoplasm. Other Wnt effectors, such as frizzled (Fzd) at the membrane and T cell factor (TCF)/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF1) transcription factors in the nucleus, are also inhibited to maintain low Wnt activity. In the Wnt on-state (right), Wnt ligands trigger the formation of the signalosome to promote Wnt signal transduction. The function of the destruction complex is inhibited, leading to the stabilization of β-catenin. β-catenin then translocates into the nucleus and binds to TCF/LEF1 to form a transcription complex along with other cofactors to initiate Wnt target transcription. LRP5/6: low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; ZNRF3: E3 ubiquitin ligase zinc- and ring-finger protein 3; RNF43: ring-finger protein 43; Dvl: disheveled; AP2: adapter protein 2; APC: adenomatous polyposis coli; CK1α: casein kinase 1α; GSK3: glycogen synthase kinase 3; Gro/TLE: groucho/transducin-like enhancer of split proteins; Pygo: pygopus; BCL9: B cell lymphoma 9 protein; Ebd1: earthbound 1; RSPO: R-spondin family of secreted ligands; LGR: leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptors; HSPG: heparan sulfate proteoglycans; SIAH1: siah E3 ubiquitin ligase 1; PP2A: protein phosphatase 2A.