Table 1.
Anticancer effects of furanocoumarins in the different reported studies.
| Furanocoumarins | Dietary Sources [2,3,4] | In Vitro | In Vivo | Anticancer Mechanisms | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Lines | Cytotoxic Concentration | Experimental Model | Dose | ||||
 Angelicin |
Parsnip | HeLa and SiHa | IC30 = 27.8 µM; IC50 = 38.2 µM | — | — | Atg3,7 and 12-5 ↑, G1/G0 arrest | [5] |
| A549 (NSCLC) | IC50~ 50 µmol | — | — | NF-κB inactivation G2/M phase arrest, cyclinB1 ↓, cyclin E1 ↓, and Cdc2 ↓; Bcl2 ↓; caspase 3,9 ↑, Bax↑ JNK ↑, ERK ↑; MMP2, MMP9 ↓, E-cadherin ↑ |
[6] | ||
| SH-SY5Y | IC50 = 49.56 μM | — | — | caspase 3,9 ↑, Bcl-2 ↓, Bcl-xL↓, and Mcl-1↓ | [7] | ||
| Caki | IC50 = angelicin (50–100 μM) and TRAIL (50 ng/mL) | — | — | caspase 3↑, c-FLIP ↓ | [8] | ||
| HepG2 and Huh-7 | IC50 = 90 ± 6.565 (HepG2); 60 ± 4.256 μM (Huh-7) | — | — | PI3K/Akt inhibition, Bcl-2↓ | [9] | ||
| — | — | Mouse liver xenograft model (BALB/c-nu/nu mice) | 50 mg/kg (16 days) | cancer cell growth ↓; p-VEGFR ↓ |
[9] | ||
 Bergamottin |
Carrot, cumin, dill, fig, grapefruit, lemon, lime, orange, parsley, parsnip | A549, H1299 | IC50 = 50–100 μM | — | — | EMT inhibition, JNK ↑; PI3K ↓, Akt↓, and mTOR kinases ↓ | [10] |
| U87 and U251 | IC50 = 2–10 μM | — | — | NF-κB inactivation, MMP9 ↓, STAT3 inhibition, Rac1 inactivation | [11] | ||
| HT-1080 | IC50 = 5–50 μM | — | — | NF-κB inactivation; MMP2, MMP9↓ | [12] | ||
| HT-29 and RKO | IC50 = 12.5 µM | — | — | caspase-3,8,9↑; PARP ↑; G2/M phase arrest, cyclinA ↓, cyclin B1↓, and Cdc2 ↓ |
[13] | ||
| A549 (NSCLC) | IC50 = 50 μM | — | — | G2/M phase arrest, cyclinA ↓, cyclin B1↓, and Cdc2 ↓ | [14] | ||
| — | — | Mouse lung xenograft model (BALB/c nude mice) | 100 mg/kg (18 days) | ↓ cancer cell growth | [14] | ||
 Bergapten or 5-Methoxypsoralen (5-MOP) |
Anise, carrot, caraway, celeriac, celery, coriander, cumin, dill, fig, grapefruit, lemon, lime, orange, parsley, parsnip, turnip | DLD-1 and LoVo | IC50 = 30 and 50 μM | — | — | G2/M phase arrest, cyclin E ↓, Cdk2 inhibition; AKT inhibition; p53 ↑, p21↑, PTEN↑ | [15] |
| MCF-7 | IC50 = 50 μM | — | — | G1-phase phase arrest, P53 ↑; AKT inhibition | [16] | ||
| Hep-G2 | IC50 = 25–50 mM | — | — | G2/M phase arrest, Cdk1 inhibition | [17] | ||
| IC50 = 25–100 μM | — | — | G2-M phase arrest, P53 ↑ and P21 ↑ | [18] | |||
| A549 (NSCLC) | 79.1 ± 2.8% (50 μM) |
— | — | G1-phase arrest, P53 ↑ | [19] | ||
| NCI-H460 | 74.5 ± 3.1% (50 μM) |
— | — | ||||
| MCF7 and ZR-75 | 50 μM | — | — | PTEN ↑, Beclin1 ↑, PI3KIII ↑, UVRAG ↑, AMBRA, LC3-I to LC3-II | [20] | ||
| HepG2 | 50 mM | — | — | PI3K/AKT inhibition, LXR (α and β)↑ | [21] | ||
| — | — | NDEA induced liver cancer (Wistar rats) |
25 and 50 mg/kg (14 days) | ↓ cancer cell growth | |||
 Bergaptol |
Carrot, grapefruit, lemon, lime, parsley, parsnip | MCF-7 | IC50 = 52.2 µM | — | — | G1-phase arrest; caspase 3,9 ↑, Bax↑, Bcl2 ↓,MMP2 ↓, MMP9 ↓, cyt c release ↑ | [22] |
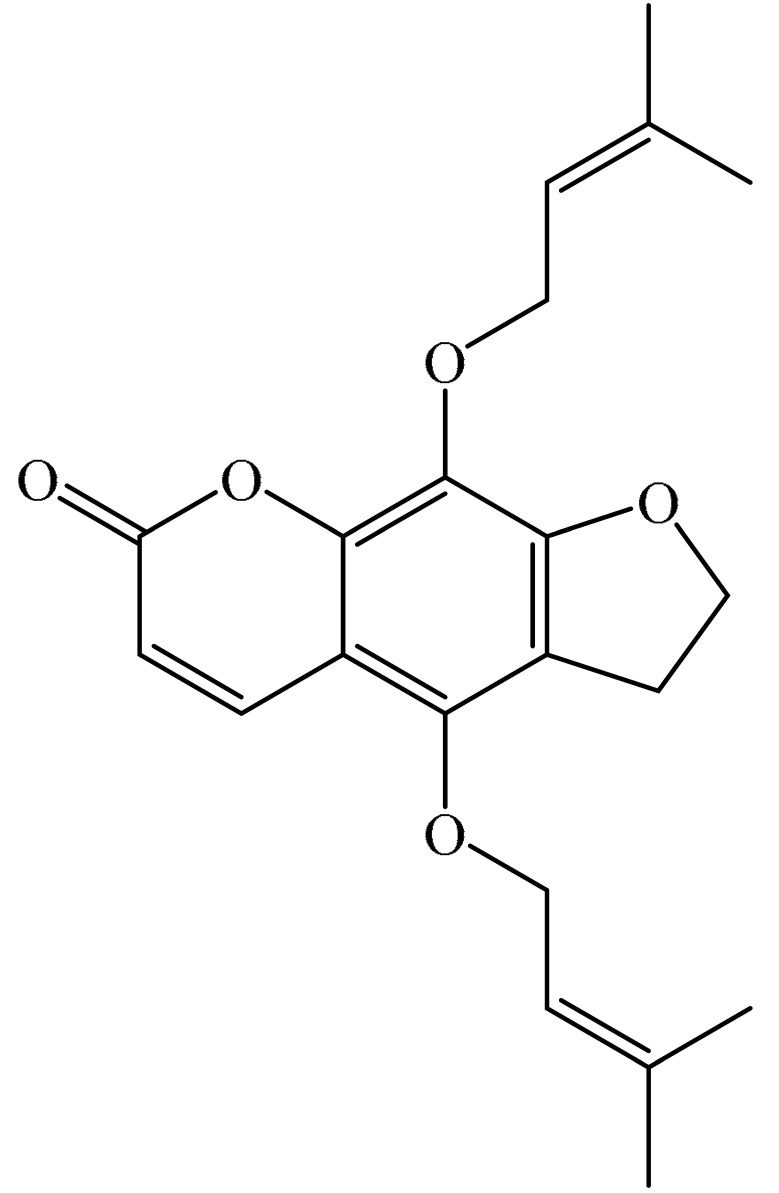
 Byakangelicol |
Lemon | HCT-15 | IC50 = 18.1 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ↓ cell viability | [23] |
| A549 (NSCLC) | IC50 =14.3 ± 0.2 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| SK-OV-3 | IC50 = 20.2 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| SK-MEL-2 | IC50 = 21.2 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| XF498 | IC50 = 28.4 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
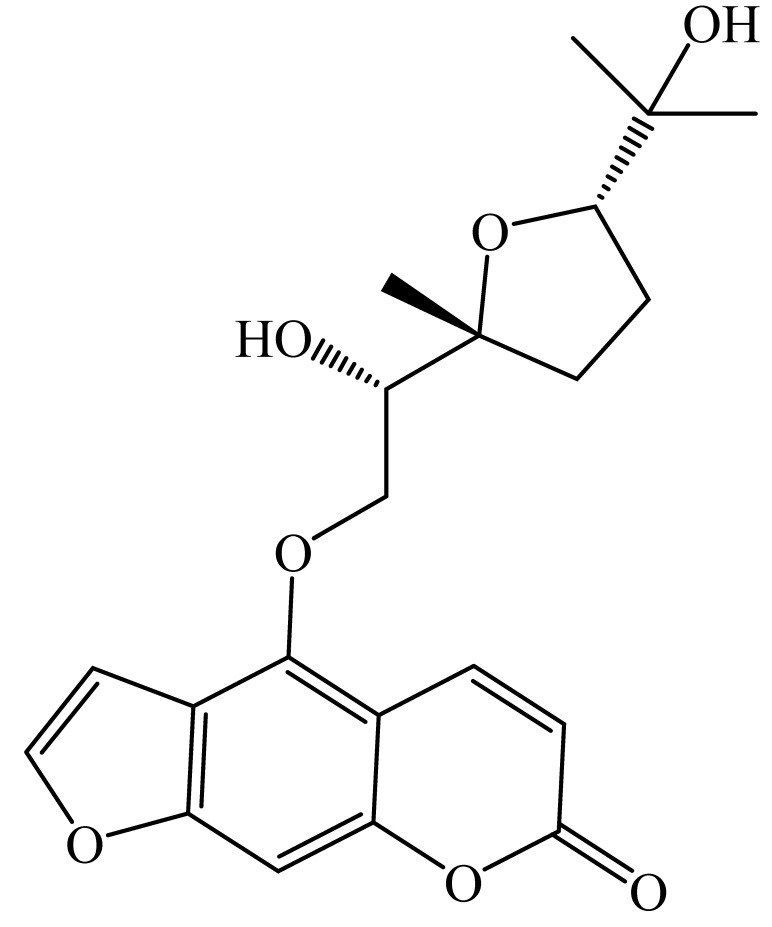
 Cnidicin |
Lemon | HCT-15 | IC50 = 7.0 ± 0.2 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ↓ cell viability | [23] |
| A549 (NSCLC) | IC50 = 6.8 ± 0.1 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| SK-OV-3 | IC50 = 8.8 ± 0.2 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| SK-MEL-2 | IC50 = 8.8 ± 0.2 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| XF498 | IC50 = 7.2 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
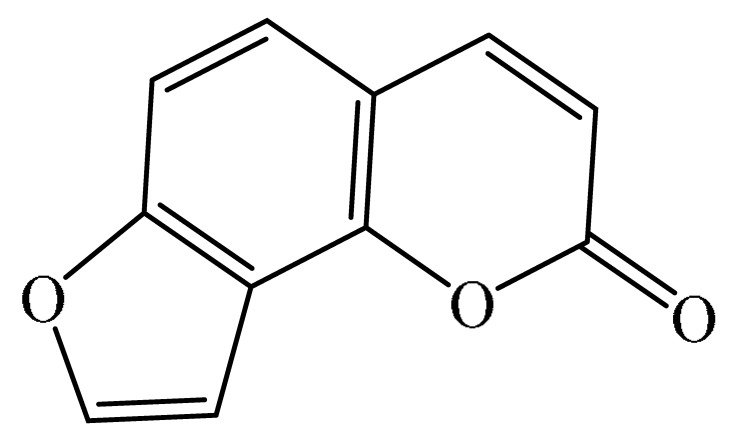
 Feroniellin A |
Feroniella lucida roots | A549 | 0.25 mM | — | — | NF-κB inactivation Atg5 ↑, Beclin1 ↑, mTOR inactivation LC3-I to LC3-II |
[24] |
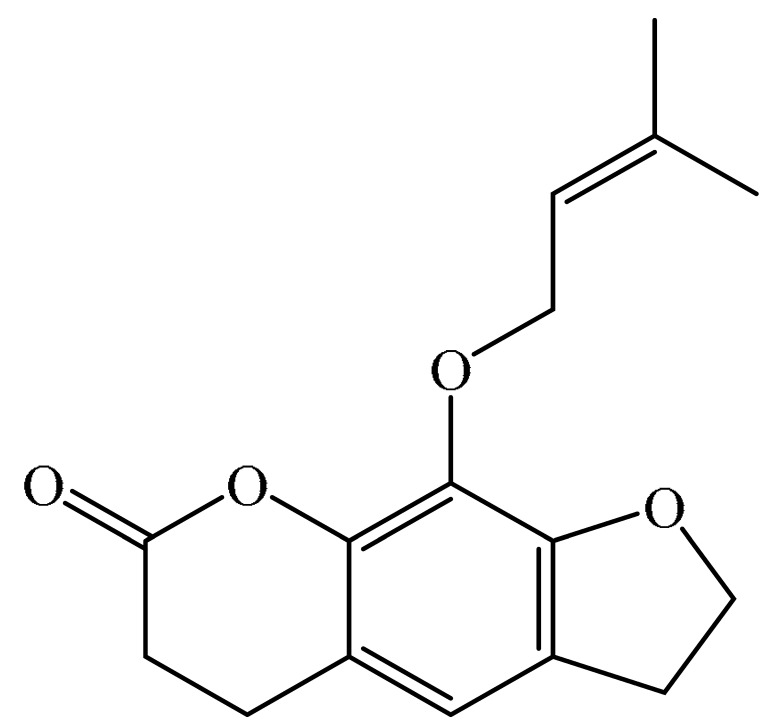
 Furanocoumarin A |
Fructus liquidambaris | A549 | IC50 = 65.28 ± 5.36 μM | — | — | P53 ↑,Bax↑, Bcl2 ↓, caspase 3 ↑ | [25] |
 Imperatorin |
Lime, parsley | SGC-7901 | IC50 = 62.6 μM | — | — | promoting G1-phase arrest; PI3K/Akt/m-TOR signaling ↓ | [26] |
| HT-29 | IC50 = 78 µM | — | — | G1-phase arrest; P53 ↑ and P21 ↑; caspase 3,7 ↑; Bcl2 ↓ | [27] | ||
| HL-60 | 10 μM | — | — | caspase 3,9 ↑; cyt c release ↑; Bcl2 ↓, PARP cleavage | [28] | ||
| H23 | 10 μg/mL | — | — | P53 ↑,Bax↑, Mcl-1↓ | [29] | ||
| HeLa | 200 μM for imperatorin and 5 μM for cisplatin | — | — | Hsp27 and Hsp72 ↓,LC3 cleavage | [30] | ||
| HCT116 | 150 μM | mTOR↓, p70S6K ↓, 4E-BP1↓, MAPK↓, HIF-1α inhibition | [31] | ||||
| HCT-15 | IC50 = 19.4 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ↓ cell viability | [23] | ||
| A549 | IC50 = 16.4 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| SK-OV-3 | IC50 =13.7 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| SK-MEL-2 | IC50 = 14.5 ± 0.2 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| XF498 | IC50 = 12.3 ± 0.5 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
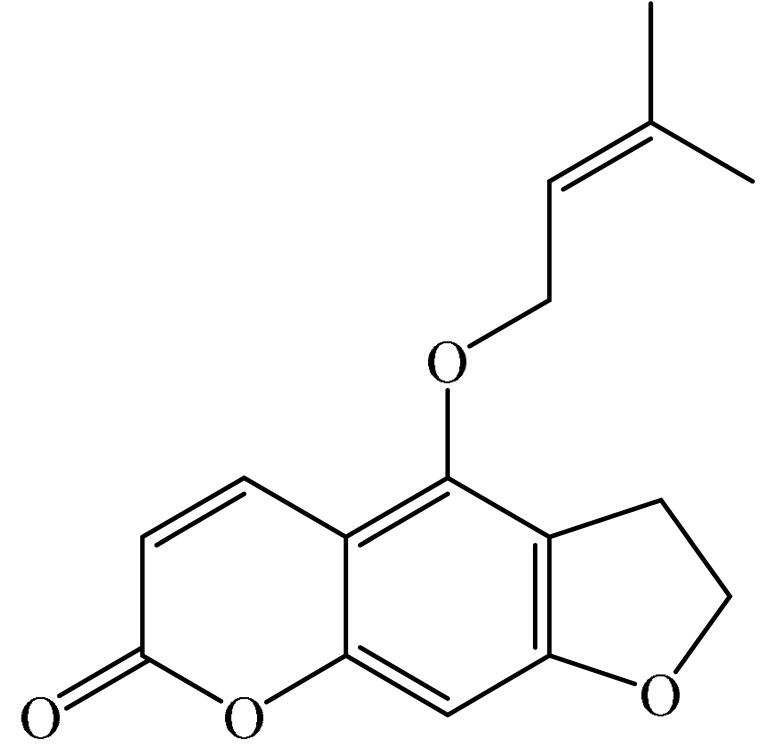 Isoimperatorin |
Lime, parsley | SGC-7901 | IC50 = 18.75 μg·mL−1 | SGC-7901 cell-induced xenograft model (mice) | 10 mg/kg (20 days) | G1-phase arrest; caspase 3,9 ↑; Bax↑, Bcl2 ↓, Survivin↓ | [32] |
| DU145 | 100 µM | — | — | G1-phase arrest | [33] | ||
| HCT-15 | IC50 = 5.6 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ↓ cell viability | [23] | ||
| A549 (NSCLC) | IC50 = 12.2 ± 0.4 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| SK-OV-3 | IC50 = 6.8 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| SK-MEL-2 | IC50 = 9.9 ± 0.2 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| XF498 | IC50 = 10.7 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
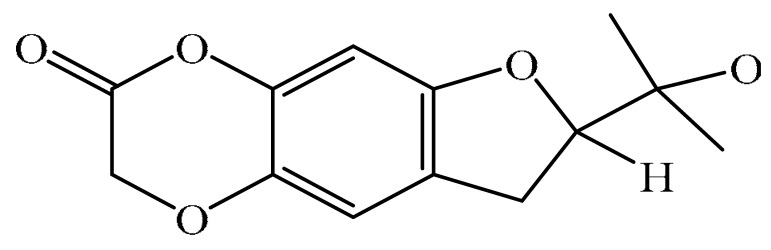 Marmesin |
Broad bean, blackberry, raspberry | U937 | IC50 = 40 µM | Mice | 30mg/kg (30 days) | Bax↑, Bcl2 ↓, Bax/Bcl-2 ratio ↑; G2/M-phase arrest | [34] |
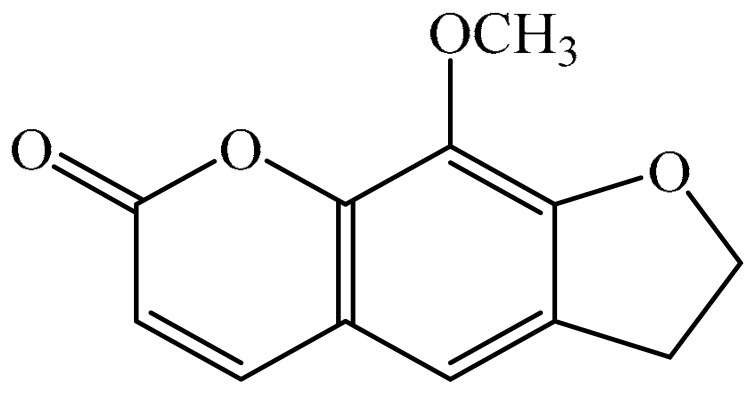 Methoxsalen/Xanthotoxin (8-MOP) |
Anise, carrot, caraway celeriac, celery, cumin, dill, grapefruit, lemon, lime, parsley, parsnip, turnip | HepG2 | 100 µM | — | — | Bax/Bcl-2 ratio ↑, MMP2 ↓, MMP9 ↓, ERK1/2 pathway inhibition, cyt c release ↑, AIF transposition ↑ | [35] |
| SK-N-AS and SW620 | IC50 = 56.3 µM for SK-N-AS and 88.5 µM for SW620 | — | — | Caspase-3,8,9↑PI3K/AKT pathway ↓, Bcl2 ↓, Bax/Bcl-2 ratio ↑ | [36] | ||
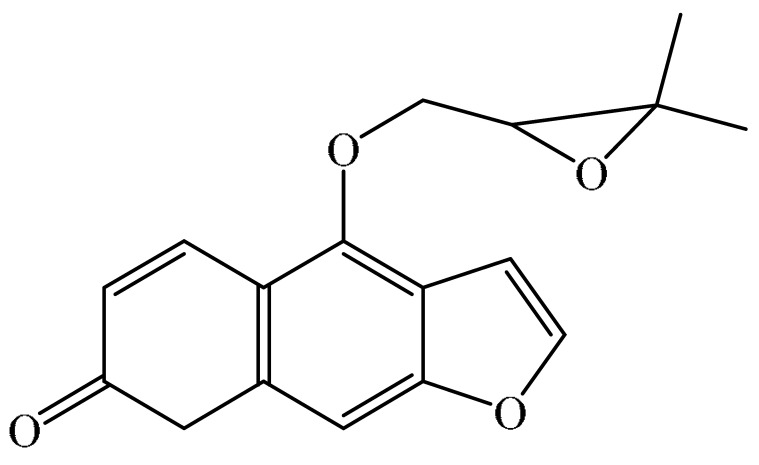 Oxypeucedanin |
Lime, parsley | L5178Y (mouse T-cell lymphoma cells) | IC50 = 40.33 ± 0.63 µM | — | — | caspase 3,9 ↑; cyt c release ↑; Bcl2 ↓ | [37] |
| HCT-15 | IC50 = 3.4 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ↓ cell viability | [23] | ||
| A549 (NSCLC) | IC50 = 9.5 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| SK-OV-3 | IC50 = 19.3 ± 0.3 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| SK-MEL-2 | IC50 = 16.5 ± 0.2 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
| XF498 | IC50 = 16.1 ± 0.5 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||||
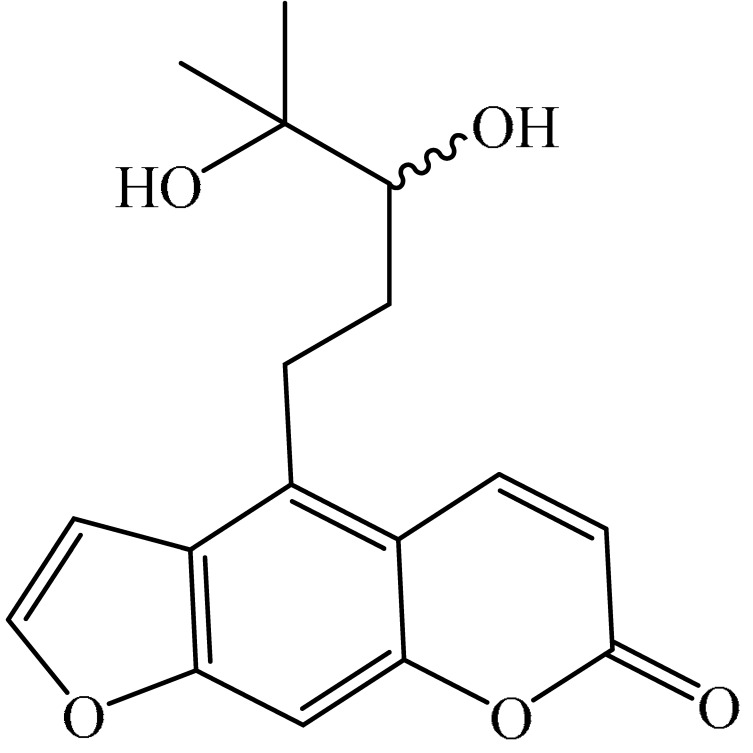 (+)-oxypeucedanin hydrate |
Angelica dahurica roots | A549, HCT-15, SK-MEL-2, SK-OV-3, XF498 | IC50 > 30 μg·mL−1 | — | — | ||
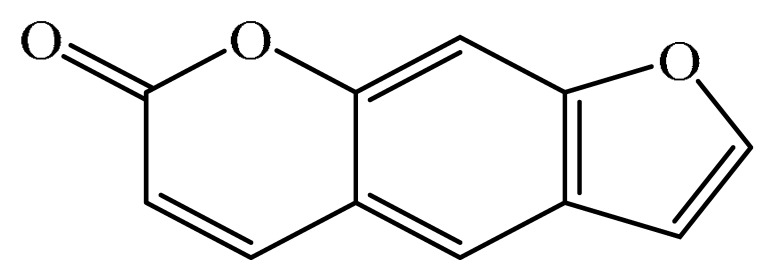 Psoralen |
Carrot, celeriac, celery, cilantro, cumin, dill, fig, grapefruit, lemon, lime, parsley, parsnip | KBv200 | 75.3% (80 μg·mL−1) | — | — | NF-κB inactivation G1/S phase arrest, c-FLIP, and IAP inhibition | [38] |
| K562 | 92.4% (80 μg·mL−1) | — | — | ||||
| MCF-7 | 17.32 ± 4.28% (8 μg·mL−1) | — | — | G1/G0 phase arrest | [39] | ||
| SMMC7721 | 40 μM | — | — | G1 phase arrest, cyclin E↓, Bax↑, Bcl2 ↓, ER stress, CHOP induction, GADD34↑, ATF4↑, GRP78↑, GRP94 |
[40] | ||
| MCF-7/ADR | IC10 = 8 μg/mL | P-gp efflux function inhibition | [41] | ||||
| IC50 = 25.59 ± 1.74 µg/mL | P-gp ATPase activity inhibition | [42] | |||||
| 43.0 µM | EMT inhibition | ||||||
| 107.5 µM | G0/G1 phase arrest | ||||||
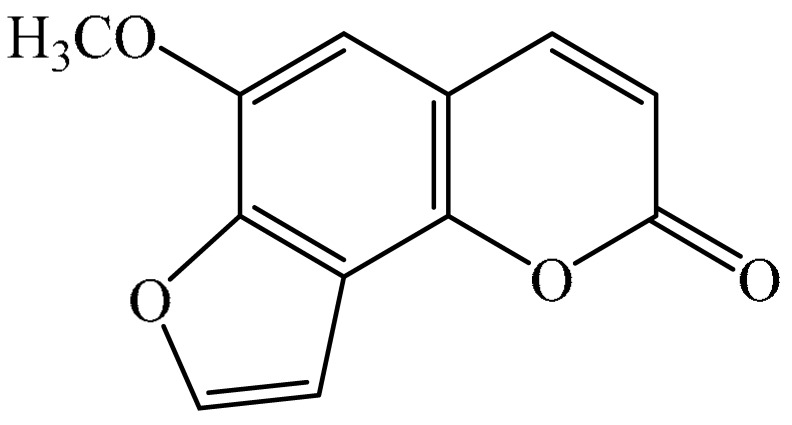 Sphondin |
Parsnip | A549 | 50 μM | — | — | NF-κB inactivation | [43] |
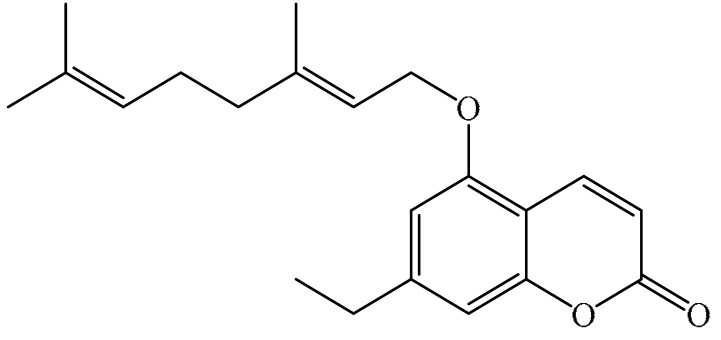 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxy-coumarin |
Lime | SW480 | 25 µM (67%) | — | — | caspase-3,8↑; Bcl2 ↓; p38 MAPK phosphorylation inhibition; G1/G0 phase arrest | [44] |
Human cancer cell lines: A549 (NSCLC), NCI-H460 (NSCLC), H23, and H1299 = lung cancer; Caki = renal carcinoma; DLD-1, LoVo, HCT-15, HT-29, HCT116, RKO, SW480 and SW620 = colorectal cancer; DU145 = prostate cancer; HL-60 = promyelocytic leukemia; HeLa and SiHa = cervical cancer; HepG2, Huh-7 and SMMC7721 = liver carcinoma; HT-1080 = fibrosarcoma; KBM-5, K562 = human chronic myeloid leukaemia; KBv200 = oral squamous carcinoma; MCF7 SKBR-3 and ZR-75 = breast cancer; SH-SY5Y and SK-N-AS = neuroblastoma; SK-MEL-2 = melanoma; SK-OV-3 = ovarian cancer; SGC-7901 = gastric cancer cell; U937 = leukemia; U87 and U251 = glioma cells; XF498 = CNS solid tumor; MCF-7/ADR = doxorubicin resistant derivatives of MCF-7 cells overexpressing P-gp; ↑ = increase; ↓ = decrease.
