Figure 1.
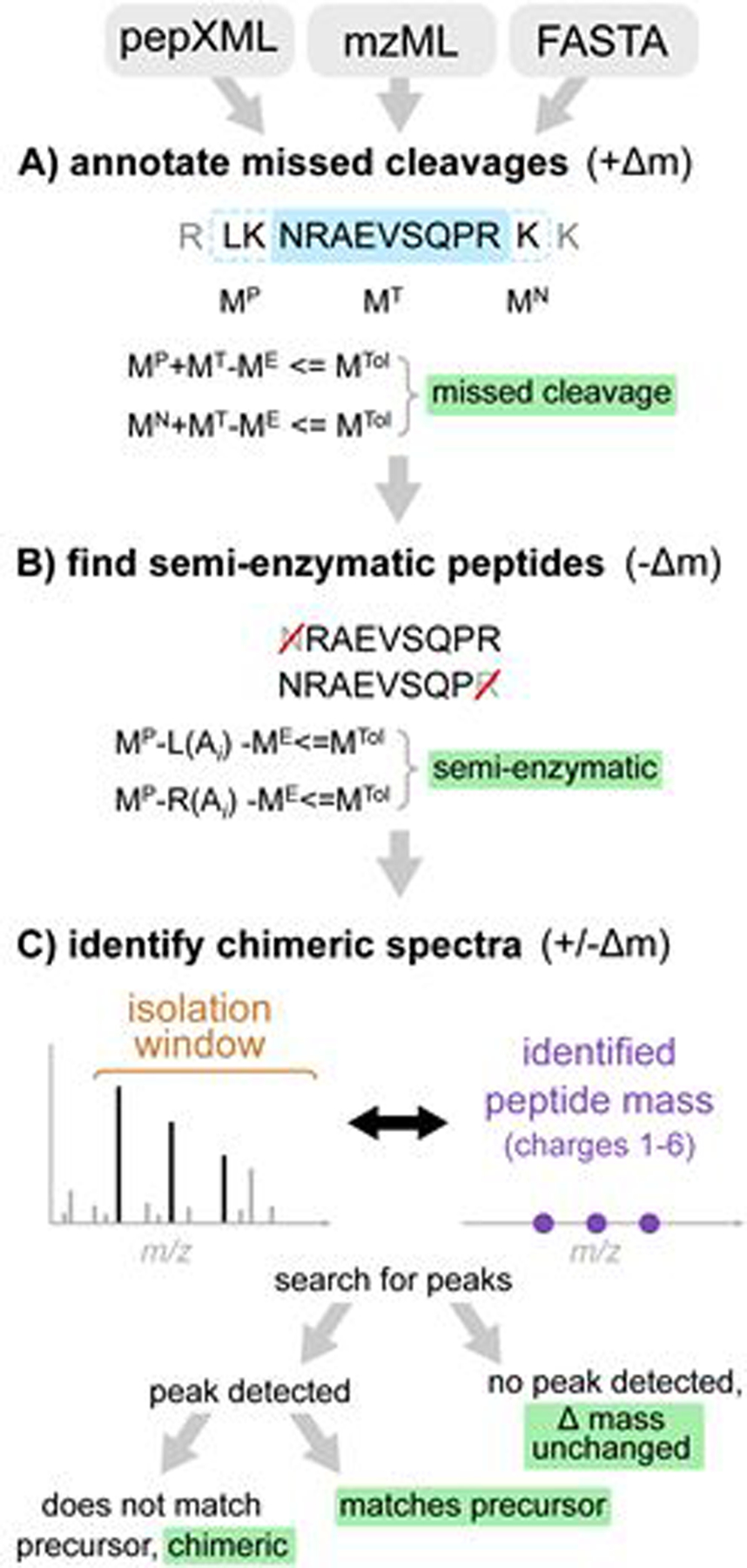
The workflow of Crystal-C as applied to each PSM from open search results. A) Find potential missed cleavage sites by searching the previous and next fully-enzymatic peptides of the identified peptide, where MTol is the mass tolerance (20 ppm by default), ME is the precursor neutral mass, MT is the identified peptide mass, and MP and MN are the previous and next adjacent fully enzymatic peptide masses, respectively. B) Check whether the PSM is semi-enzymatic by deleting one amino acid from the left or right side of the identified peptide sequence at a time and calculating the mass difference between ME and the remaining peptide sequence. If the mass difference is smaller than MTol, the remaining peptide sequence is regarded as semi-enzymatic. C) Find chimeric MS/MS spectra. Crystal-C searches for peaks from the identified peptide within the isolation window by comparing theoretical isotopic clusters (purple)to the MS1 spectrum. If a peak matching one of the theoretical isotope clusters is found in the isolation window and does not belong to the precursor, the PSM is considered chimeric.
