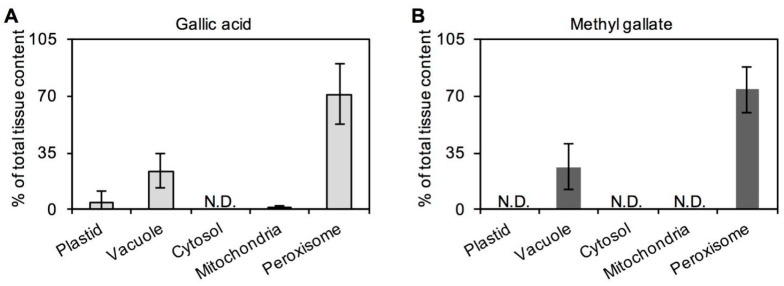
Figure 3.
Subcellular distributions of (A) gallic acid and its (B) derivative methyl gallate in tea leaf tissue. Tea leaves were from Camellia sinensis cv. Jinxuan plant. The tissues of tea leaf were fractionated using a nonaqueous procedure. Gallic acid and methyl gallate in each fraction were measured by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography. The subcellular distributions were calculated by comparing the metabolite and marker enzyme distributions using Bestfit software. Data expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 2). N.D.—not detected.