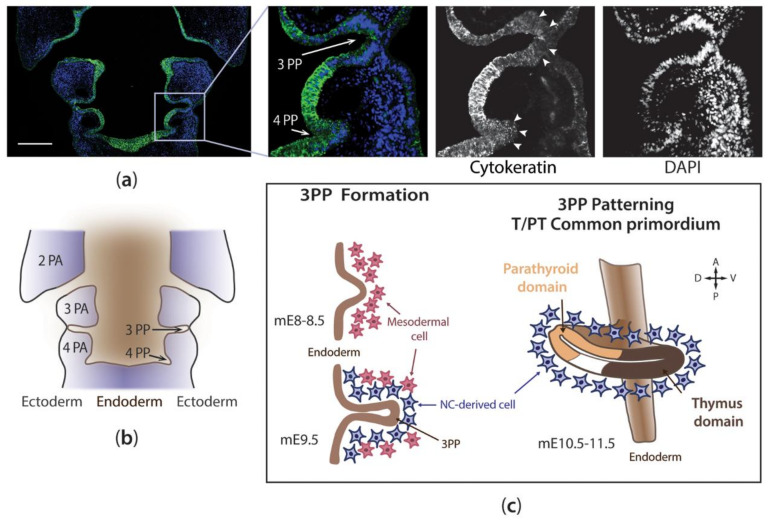
Figure 2.
The early stages of thymus development. Hemi-coronal section of the pharyngeal region of a chicken embryo immunodetected with cytokeratin antibody (clone AE1/AE3, which binds to cytokeratin 1–8, 10, 14–16, and 19), at E4, a stage prior to Foxn1 expression. Cytokeratin-positive endoderm and ectoderm cells are observed. The columnar epithelium of the pouches is indicated by white arrowheads in the magnified images (a). Schematic representation of coronal section (a), detailing PP and PA locations (b). Schematic representation of the cellular interactions between the endoderm and surrounding mesenchymal cells during the early stages of thymus organogenesis in the mouse model (c). See main text for details. Color code: Endoderm-, mesoderm-, and NC-derived cells in brown, rose, and blue, respectively. A—anterior; D—dorsal; mE—embryonic day of development in the mouse; NC—neural crest; PA—pharyngeal arch; PP—pharyngeal pouch; P—posterior; T/PT—thymus/parathyroid glands; V—ventral. Scale bar, 200 μm.