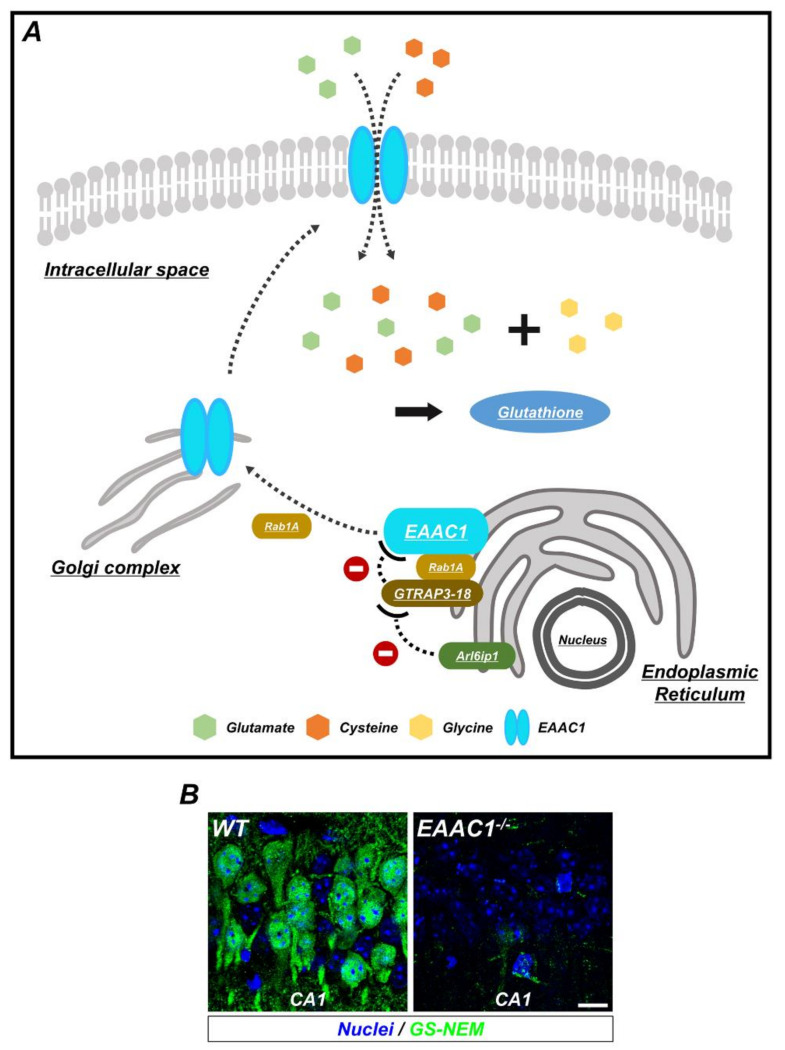
Figure 2.
The synthesis of glutathione (GSH) by EAAC1/glutamate transporter-associated protein 3-18 (GTRAP3-18) in neurons. (A) GSH is composed of three amino acids: Glycine, cysteine, and glutamate. To increase the synthesis of GSH, EAAC1 is translocated to the plasma membrane and transports cysteine and glutamate into the neuron. Ras-related protein Rab1A regulates several membrane-trafficking pathways, including EAAC1 transport from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi apparatus, which is interfered with when GTRAP3-18 binds to Rab1A. In addition, GTRAP3-18 directly retains EAAC1 in the ER to inhibit the synthesis of GSH. Thus, Arl6ip1, a GTRAP3-18-interacting protein, reduces GTRAP3-18/EAAC1 interaction and positively regulates EAAC1-facilitated glutamate transport. (B) Immunofluorescence images showing the GSH-N-ethylmaleimide (GS-NEM) adducts in the neurons of hippocampal CA1 from WT and EAAC1−/− mice. EAAC1−/− mice (3–5 months old; weight 25–35 g) showed neuronal GSH deficiency. Scale bar = 10 µm.