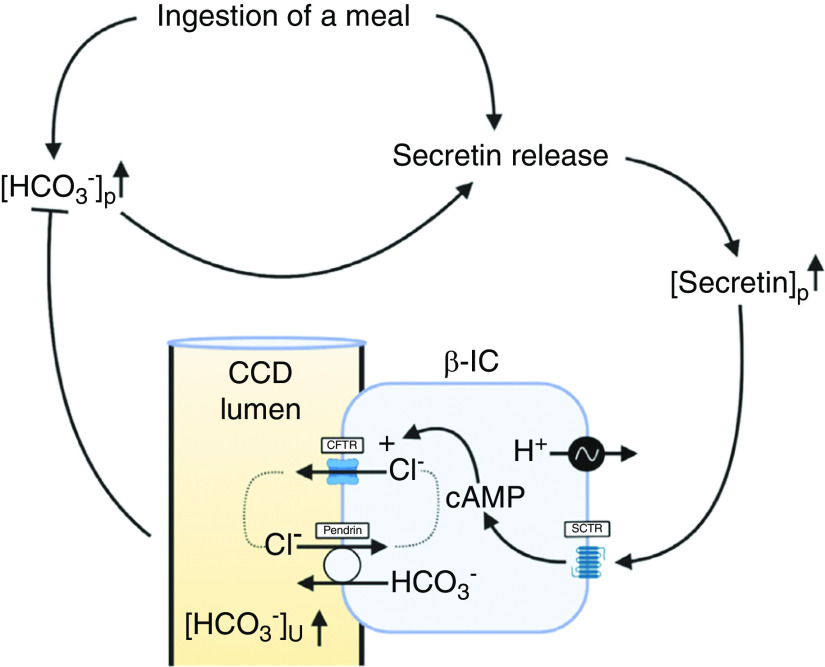
Figure 9.
Secretin-release is stimulated by alkalosis and triggers HCO3- secretion in the CCD. Schematic illustration of the proposed mechanism of secretin-induced urinary HCO3− excretion. Ingestion of a meal will cause a transient alkalosis. Ingestion of a meal itself and/or metabolic alkalosis stimulates secretin release. This will increase plasma concentration of secretin ([secretin]p). An increased plasma concentration of secretin will activate HCO3− secretion by β-ICs in the CCD. This will increase urine pH and [HCO3−] excretion and thereby help compensate metabolic alkalosis. This image was created with BioRender.com.