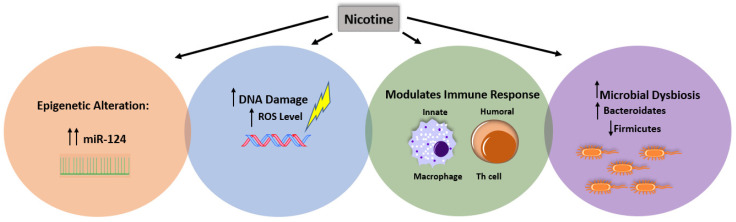
Figure 1.
Effect of multi-factorial interaction and nicotine on IBD pathogenesis. Illustration of how nicotine may regulate the pathogenesis of IBD by stimulating DNA damage in intestinal cells, inducing microbial dysbiosis and increasing susceptibility to infection, increasing the probability of epigenetics, and modulating intestinal immune response.