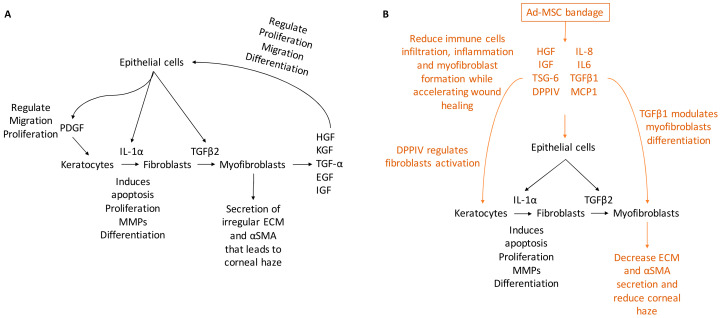
Figure 8.
A schematic representing corneal wound healing. (A) Upon injury, a cascade of growth factors and cytokines released by the epithelial and stromal cells that plays an essential role in wound healing, such as IL-1α, PDGF, HGF, KGF, TGF-α, EGF, and IGF. IL-1α and PDGF are produced by the epithelial cells to mediate stromal cell response by inducing cells at the edge of the wound to undergo apoptosis while others proliferating secret MMPs and transdifferentiating into fibroblast. Epithelial cells also produce TGFβ2 that regulate cells transdifferentiating to myofibroblasts that secret irregular ECM and αSMA, which leads to corneal haze. (B) Ad-MSCs are able to produce paracrine factors from within the bandage that accelerate wound healing and reduce inflammation, such as IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 that regulate inflammatory response; DPPIV regulates fibroblasts activation and TGFβ1 that modulate myofibroblasts differentiation. Thus, the addition of Ad-MSCs reduces corneal haze and improves healing.