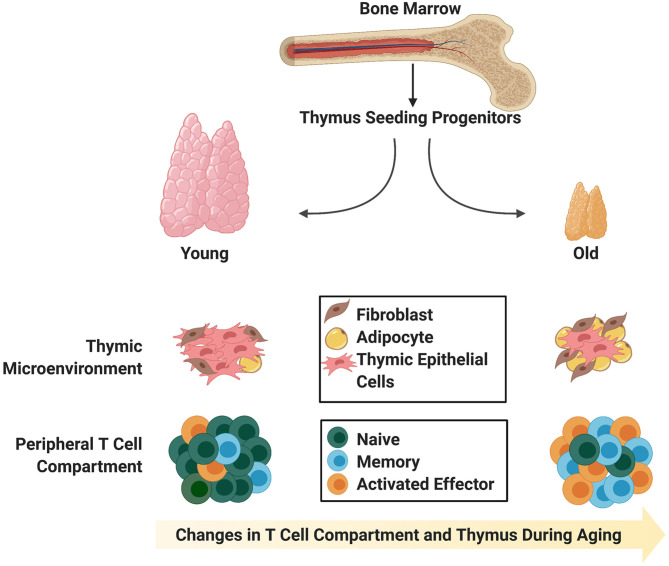
Figure 1.
Age-associated changes in the thymic stromal and T cell compartments. The young thymus is mainly comprised of thymic epithelial cells (medullary and cortical; not distinguished) capable of supporting rigorous thymopoiesis of naïve T cells with T cell receptor diversity. Naïve T cells comprise the largest proportion of peripheral T cells in young individuals. In contrast, the involuted aged thymus contains adipocytic and fibrotic cells, and the reduction in thymic epithelial cells and physical changes in thymic morphology do not support robust generation of naïve T cells with T cell receptor diversity. Instead, there is an enlargement in the peripheral memory T cell compartment, which is capable of giving rise to effector T cells upon stimulation.