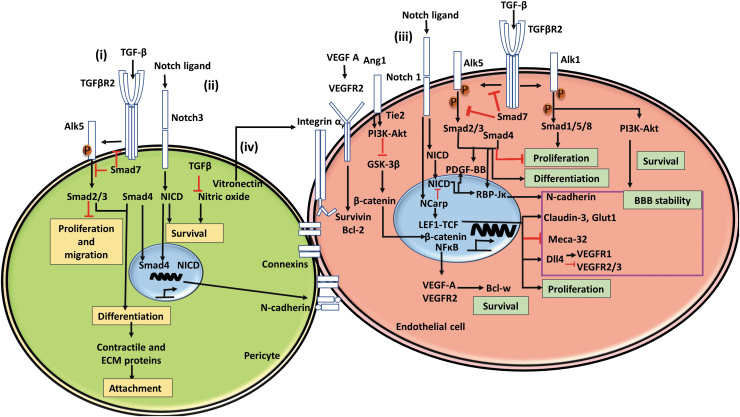
FIG. 2.
The interactions of pericytes with endothelial cells. (i) The roles of TGF-β pathway. In both pericytes and endothelial cells, TGF-β binds to TGFβR2, which subsequently phosphorylates Alk5, activating Smad signaling cascades that play a vital role in cell function such as proliferation, migration, differentiation, and expression of contractile and ECM proteins. In addition, TGF-β inhibits nitric oxides and promotes cell survival. (ii) The role of Notch signaling in pericytes and endothelial cells. Notch ligands bind notch, leading to translocation of NICD and the Smad cascade, which work synergistically to promote N-cadherin expression, increasing BBB stability. (iii) In endothelial cells, VEGF A binds VEGFR, affecting cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation. Furthermore, Alk5 works synergistically with Notch signaling and Tie2 downstream signals to promote BBB stability. Pericytes directly affect this process through Ang1-Tie2 signaling. (iv) Pericytes also secrete vitronectin, which interacts with integrin αv, resulting in transcriptional activities. Adapted from Sweeney et al.11 ECM, extracellular matrix; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; NICD, Notch intracellular domain. Color images are available online.