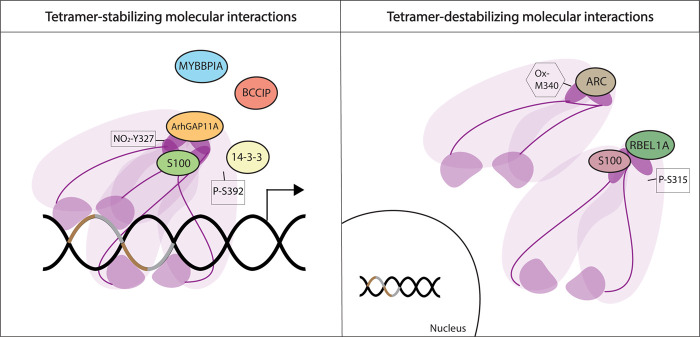
Figure 2.
Regulation of p53 oligomeric state. Protein interactions and posttranslational modifications (PTMs) regulate p53 oligomerization by either stabilizing p53 tetramers or inhibiting their formation. Interacting proteins are depicted as circles. Only ArhGAP11A and some S100 members have been shown to directly bind the p53 TD and stabilize it. ARC, RBEL1A, and other S100 members bind directly to the p53 TD and impede tetramer formation (exemplified here as steric blockage of oligomerization of two dimers). Some PTMs also regulate tetramer formation, positively or negatively (nitration [NO2], oxidation [Ox], and phosphorylation [P]). Purple denotes p53, TD is dark purple color (see Fig. 5, below). Brown and gray DNA pieces denote a p53 response element.