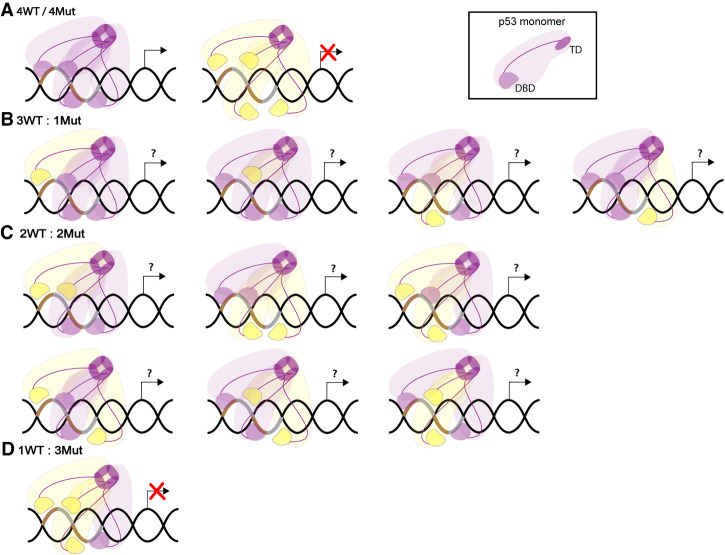
Figure 5.
Mutant and WT p53 form mixed tetramers. (A) Homotetramers of p53 WT (purple) or p53 DBD mutant (yellow) proteins are formed when these have a functional TD. p53 WT tetramers allow efficient binding to p53 response element (brown and gray DNA segments) and are transcriptionally functional, while mutant tetramers are not. (B) Mixed tetramers composed of three p53 WT and one p53 DBD mutant proteins. (C) Mixed tetramers composed by two p53 WT and two p53 DBD mutant proteins. (B,C) Locations of mutant proteins can vary and potentially have different impacts on transcription. (D) Mixed tetramers composed of one p53 WT and three p53 DBD mutant proteins are transcriptionally inactive (Chan et al. 2004).