Figure 4.
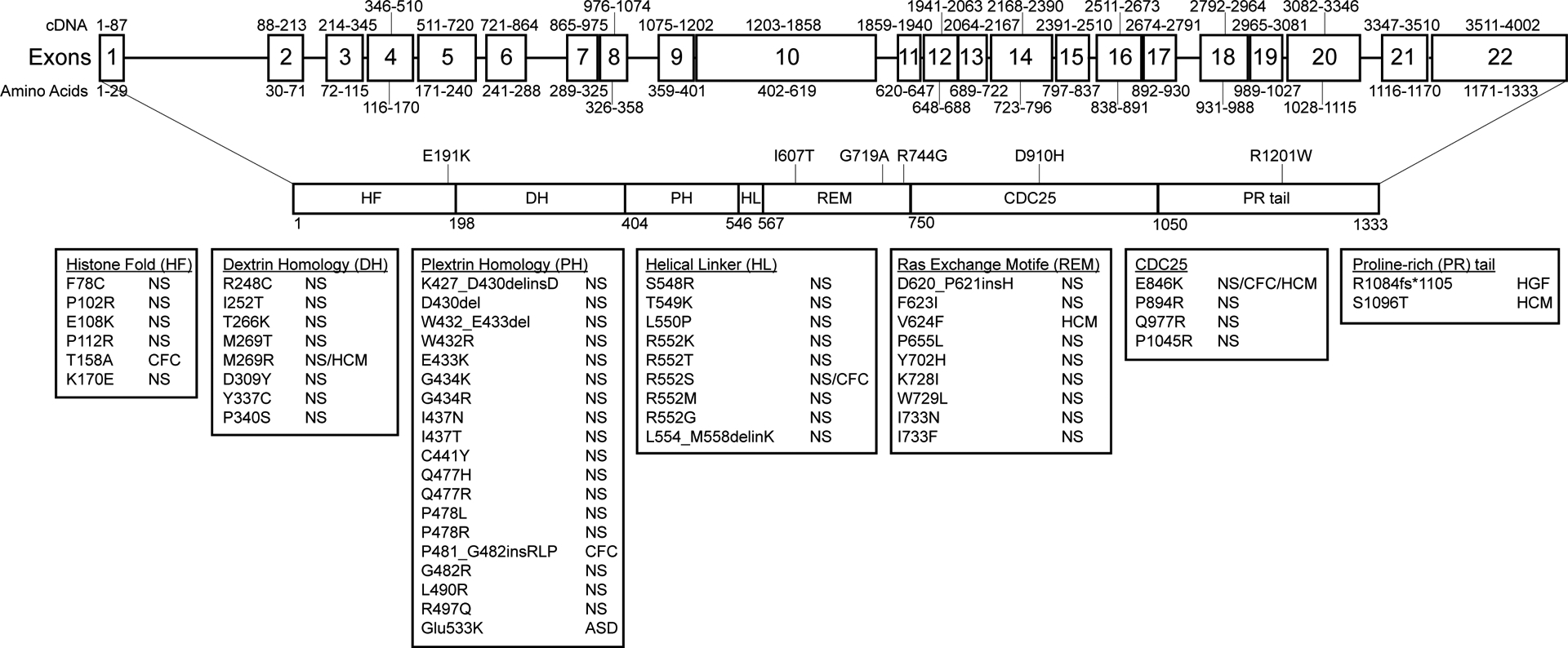
SOS1 gene and protein structure. The SOS1 gene and protein structure is shown. SOS1 is encoded by 22 exons spanning a total of 1333 amino acids and 6 functional domains roughly divided into two functional halves by a short helical linker. Positions and disease associations of reported SOS1 variants are indicated. DCM-associated variants identified in this study are indicated and summarized in Table 1. SOS1 natively exists in an auto-inhibited state that is regulated by a primary N-terminal regulatory unit comprised of a histone-like fold (HF) domain, a Dbl homology (DH) domain, and a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. Together these domains prevent RAS binding and activation at the C-terminal domains when SOS1 is not actively bound at the plasma membrane. Membrane association is primarily carried out by the proline rich (PR) tail through direct interactions with SH3 domains of GRB2. Two other C-terminal domains, a RAS-exchange motif (REM) and a CDC25 domain, together act as the catalytic core of the SOS1 protein. Alleviation of auto-inhibition following membrane association frees the REM to bind to RAS. Conformational changes promote binding of a second RAS molecule at the adjacent CDC25 catalytic site initiating GDP/GTP exchange and RAS activation. Abbreviations: ASD, Atrial septal defect; CFC, Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome; HCM, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; HGF, hereditary gingival fibromatosis; NS, Noonan syndrome.
