Figure 5.
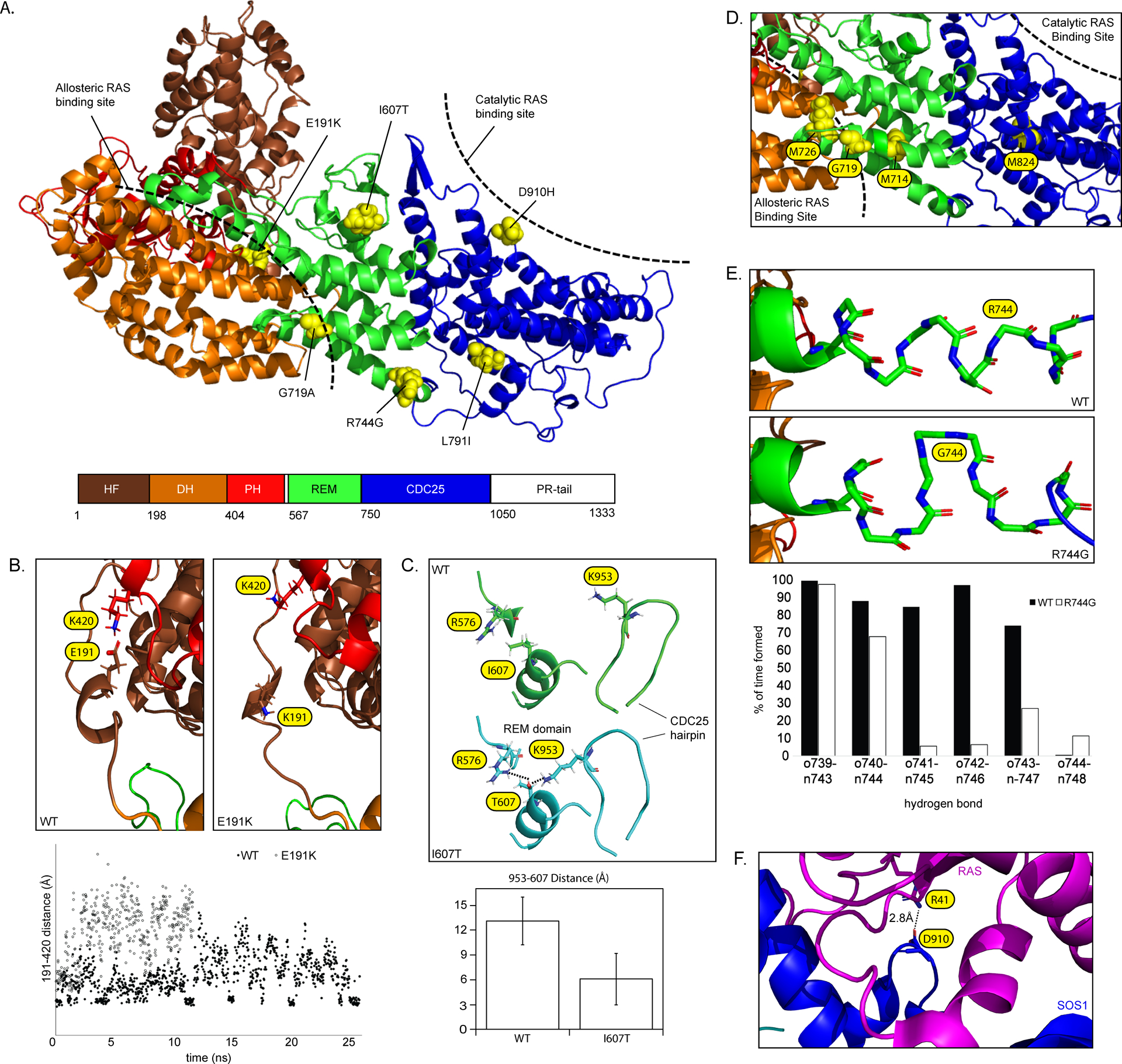
(A) SOS1 domain organization (PDB: 3KSY). Positions of DCM-associated variants identified in this study are indicated. Hatched bars indicate approximate allosteric and catalytic RAS binding sites. (B) Modeling of the wild-type SOS1 suggests the presence of an intermittent electrostatic association between Glu191 and Lys420 (evidenced by multiple short-lived 4 Å distance measurements) that is absent in models of p.(Glu191Lys). (C) Modeling of p.(Ile607Thr) suggests a hydrogen bond rearrangement between the region surrounding Ile607 and the neighboring CDC25 helical hairpin . The addition of an –OH group promotes interactions between both Arg576-Thr607 and Lys953-Thr607 (left) and reorients the CDC25 helical hairpin closer to the REM domain (right). The bar graph displays reduced average distance from the end of the sidechain of Lys953 to Thr607. Average distances with standard deviations represent 1100 independent measurements compiled over 25ns (D) p.(Gly719Ala) is positioned between the allosteric and catalytic RAS binding sites. Other amino acids within this same helix are involved in allosteric changes to the REM domain following RAS binding27. (E) Modeling of p.(Arg744Gly) demonstrates a localized unwinding of the surrounding helix by about 1 turn. (F) Asp910 is located at the SOS1-RAS interface and directly associates with Arg41 of the RAS Switch 1 region28.
