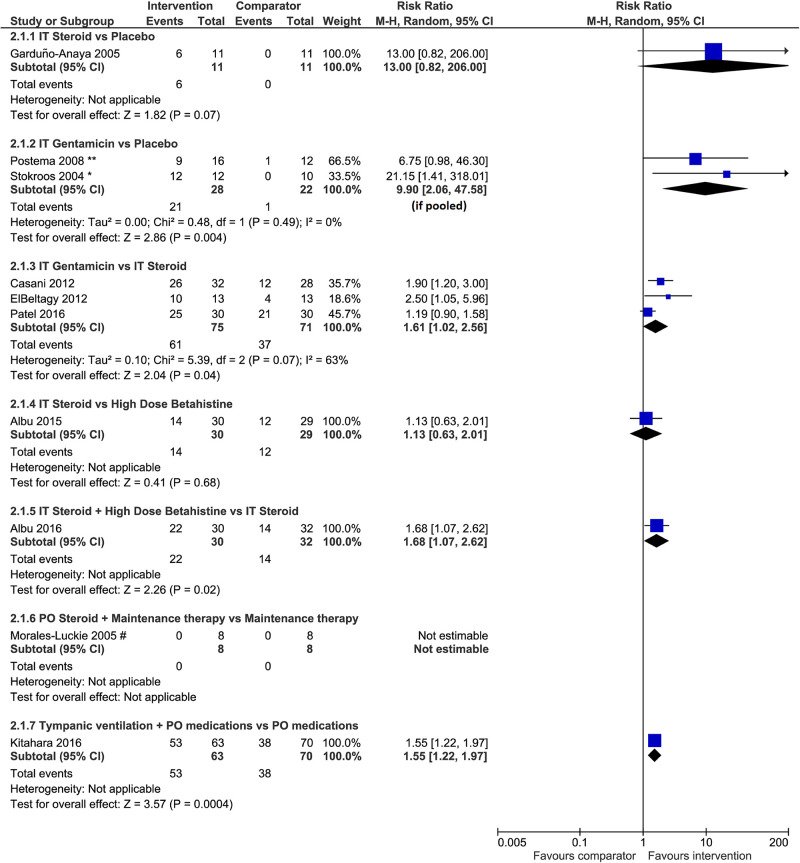
Fig 6. Risk ratio of complete vertigo control versus other categories as per the 1995 AAO-HNS definition.
The AAO-HNS classes for vertigo control include complete (class A: numeric value 0) or substantial control (class B: 1–40), limited control (class C: 41–80), insignificant control (class D: 81–120), worse control (class E: >120), and secondary treatment initiated due to disability from vertigo (class F). * In Stokroos and Kingma [50], the number of patients with no complaints of vertigo attacks 6 weeks after the last treatment and during follow-up (6–28 months) had been used. ** In Postema et al [46], the number of patients with no complaints of vertigo (0 of a vertigo score which ranged 0 to 3) 12 months after treatment had been used. # In Morales-Luckie et al [48], maintenance therapy in both groups consisted of diphenidol (25 mg/d) plus acetazolamide (250 mg/48 h) and a low-sodium diet (< 1500 mg/d). Only patients with limited vertigo control (Class C) and severe disability (Scale 3) were included.