Figure 2. .
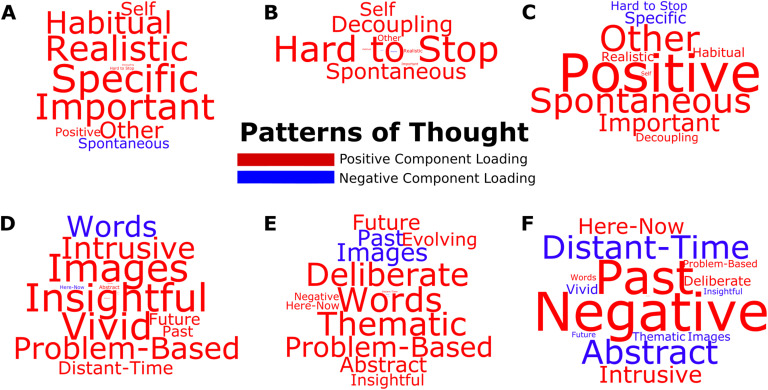
Decomposing distinct patterns of thought. Following the initial hierarchical clustering of the participants’ ratings on the experience sampling questionnaire, a total of six patterns of thought were identified using PCA. Three principal components in each of the two clusters explained 51% and 35% of the variability in the data, respectively. The Varimax rotated component loadings are visualized using word clouds. While the size of the text refers to the relative strength of the component loadings, positive and negative loadings are indicated via red and blue fonts, respectively. The components highlighted (A)important/specific thoughts, (B) perceptually decoupled/hard-to-stop thoughts, (C) positive/spontaneous thoughts, (D) insightful/image-based thoughts, (E) deliberate/verbal thoughts, and (F) negative/past-related thoughts. The individual variation on these patterns of thought were carried forward on to the NBS analysis as between-subject explanatory variables.