Figure 3.
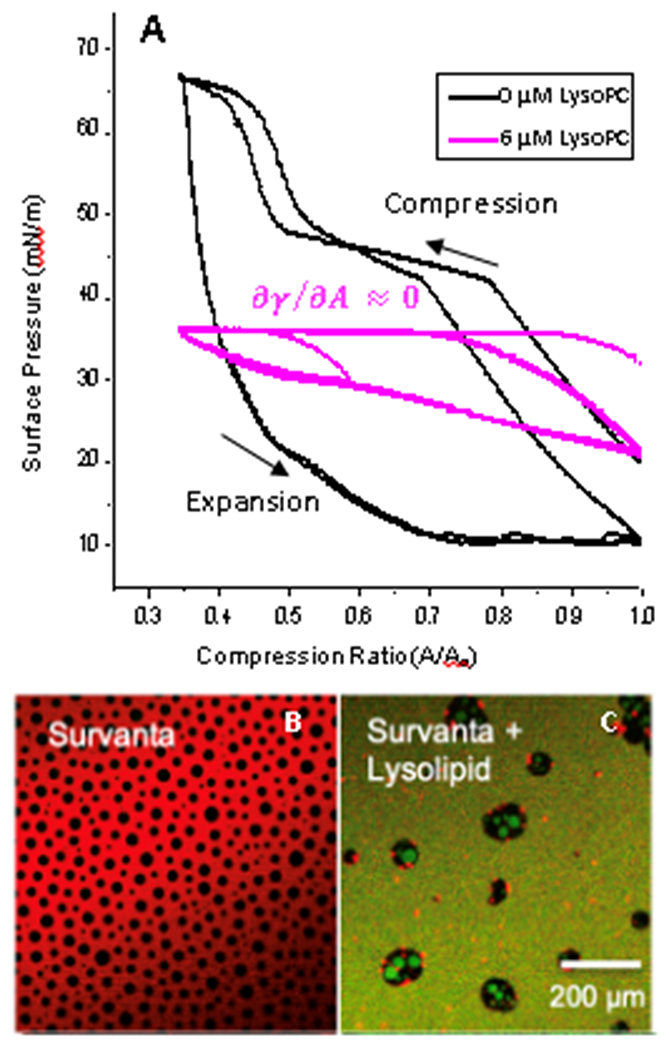
A) The clinical lung surfactant, Survanta on a saline subphase in a Langmuir trough repetitively reaches πmax~66 mN/m on cyclic compression (black). Fluorescence images of this film are shown in B). LysoPC at its CMC of 6 μM in the subphase decreases the maximum surface pressure to 36 mN/m (pink), which is the equilibrium surface pressure of a pure LysoPC monolayer 1. Fluorescence images of this monolayer are shown in C).
B) Fluorescence image of Survanta labelled with Texas Red DHPE on saline subphase. The dye preferentially locates in fluid regions of the monolayer generating the red contrast. Crystalline domains appear black {Sachan, 2018 #1204}. C) Dynamic compression and expansion of Survanta on the LysoPC containing subphase leads to displacement of the Survanta from the interface in favor of green labelled LysoPC. The green LysoPC is homogeneously distributed in the fluid regions and even appears to displace the solid phase of Survanta. The surface pressure (pink curve in A) is independent of compression, or and , leading to the Laplace instability.
