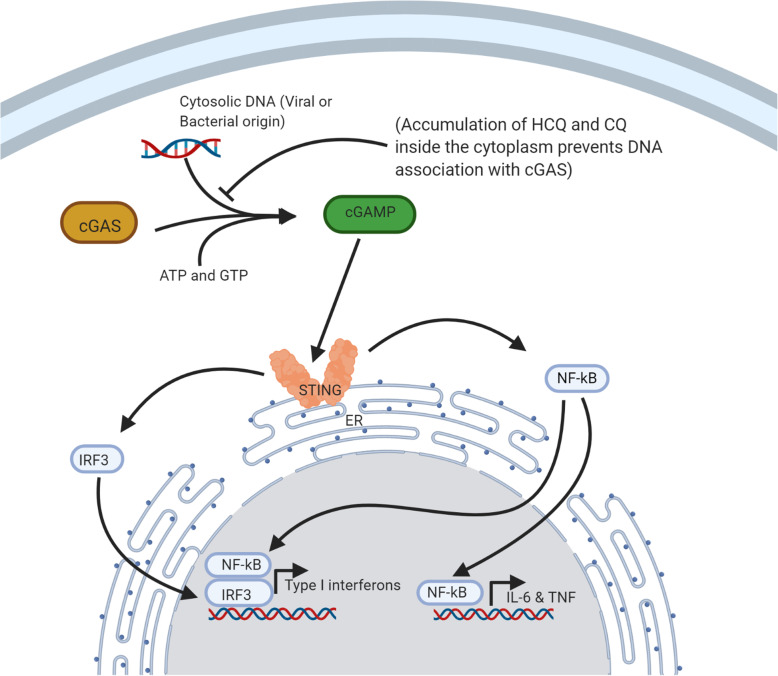
Fig. 6.
cGAS-STING Pathway inhibition by HCQ and CQ: DNA sensor cGAS (cyclic GMP-AMP synthase) can recognize DNA of viral/bacterial origin and synthesize a dinucleotide molecule, cGAMP (2′, 5′-cyclic GMP-AMP dinucleotide). Newly synthesized cGAMP can activate an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated protein STING (Stimulator of interferon genes). STING potentially activates the transcription factors IRF3 and NF-kB, which can then migrate to the nucleus and lead to the transcription of type I IFNs and cytokines. Although HCQ/CQ doesn’t directly bind to the active site of cGAS, these molecules can occupy the minor grooves of DNA molecule and prevent association with cGAS