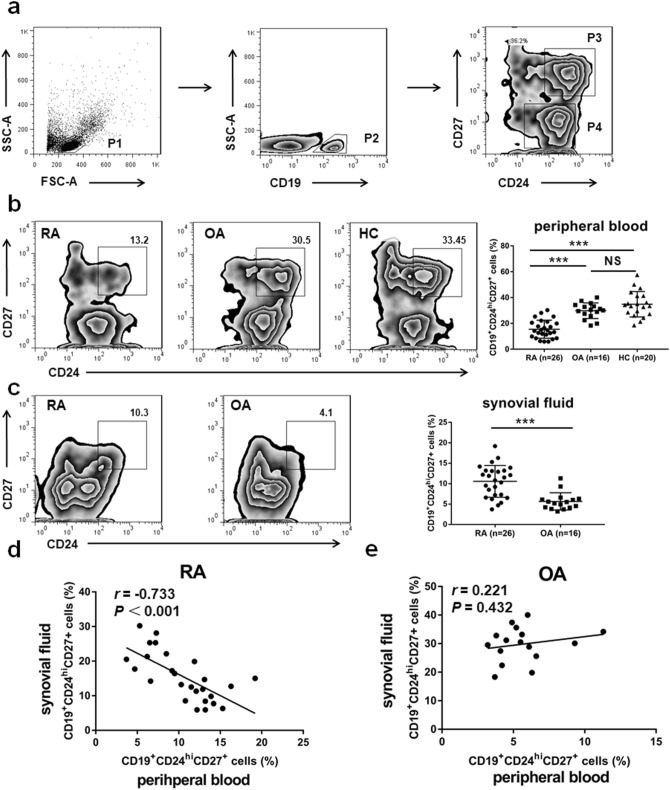
Figure 1.
Increased SF CD19+CD24hiCD27+ B cells were inversely correlated with PB CD19+CD24hiCD27+ B cells in patients with RA. Representative flow cytometry charts depicting the gating strategy for CD19+CD24hiCD27+ B cells (P3) in healthy PB (a). The percentage of PB CD19+CD24hiCD27+ B cells was analyzed in 26 patients with RA, 16 patients with OA and 20 healthy controls (HC) (b). The proportion of SF CD19+CD24hiCD27+ B cells was assessed by flow cytometric analysis in 26 RA and 16 OA patients (c). The correlations between the percentage of SF CD19+CD24hiCD27+ B cells and paired PB CD19+CD24hiCD27+ B cells of RA patients (n = 26) (d) and OA patients (n = 16) (e) were evaluated respectively. ***p < 0.001; NS, not significant.