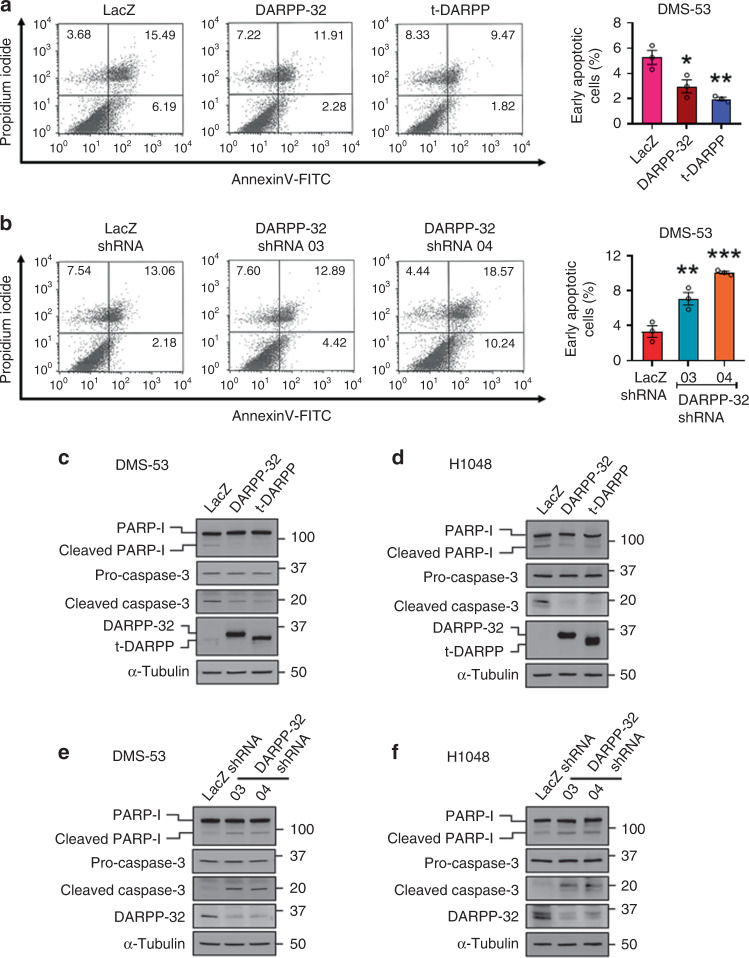
Fig. 1. DARPP-32 and t-DARPP decrease cell death by reducing apoptosis.
a Retrovirus containing control- (LacZ), DARPP-32- or t-DARPP-overexpressing clones and b lentivirus encoding control (LacZ) or DARPP-32 shRNAs were transduced in DMS-53 cells. Cells were incubated with anti-annexin V antibodies conjugated with FITC followed by propidium iodide incorporation. Flow cytometry-based apoptosis assays were performed to determine the total number of annexin V-positive cells. The average number of annexin V-positive cells of three independent experiments were plotted in a bar graph. Each open circle on a graph represents an independent experiment. The numerical values on quadrants of the scatter plots represent the percentage of total cells in one single representative experiment. c DMS-53 and d H1048 cells were transduced with control-, DARPP-32- or t-DARPP-overexpressing clones. Cell lysates were collected and immunoblotted with antibodies to detect cleaved and uncleaved PARP-I, cleaved and uncleaved (i.e., pro-) caspase-3, DARPP-32 and α-tubulin (loading control). e DMS-53 and f H1048 cells were transduced with lentivirus encoding control or DARPP-32 shRNAs. Cleaved and uncleaved PARP-I, cleaved and uncleaved (i.e., pro-) caspase-3, DARPP-32 and α-tubulin (loading control) proteins were detected by immunoblotting of cell lysates. Immunoblots are representative of three independent experiments. All bar graphs represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test for multiple comparison.