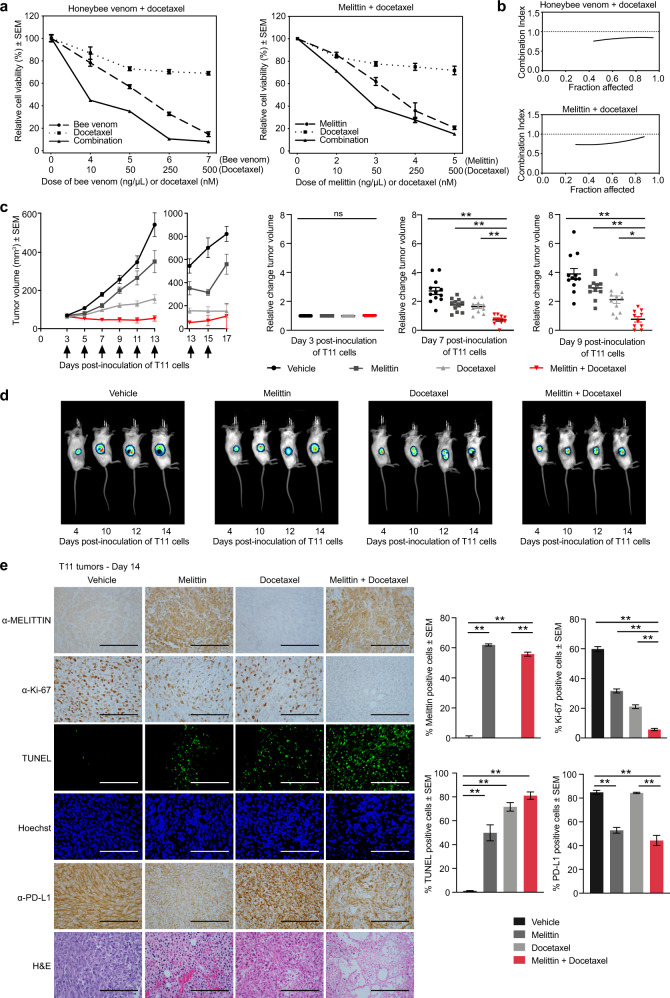
Fig. 5. Melittin sensitizes highly aggressive TNBC tumors to docetaxel treatment in vivo.
a Cell-viability assays of T11 cells treated with honeybee venom and melittin alone and in combination with docetaxel for 24 h. Representative plots of the combination treatments are presented (n = 3). b Combination index graphs obtained for different fractions of cells affected in each combination, calculated using CompuSyn software. c Tumor volumes of mice treated intratumorally with vehicle, 5 mg/kg melittin, 7 mg/kg docetaxel, and 5 mg/kg melittin + 7 mg/kg docetaxel. Arrows indicate the treatment days. Corresponding scatter plots of relative change in tumor volumes at days 3, 7, and 9 are indicated (one-way ANOVA, n = 12). d Representative bioluminescence imaging (BLI) of T11-luciferase tumors in mice at days 4, 10, 12, and 14 post inoculation of the cells. e Representative images of immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence in tumor biopsies from mice extracted on day 14 post T11 inoculation stained with anti-melittin, anti-Ki-67, TUNEL assay, Hoechst, anti-PD-L1, and H&E (one-way ANOVA, n = 8). Scale bars represent 100 µm. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Differences were considered significant at p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), and p < 0.001 (***). See also Supplementary Figs. 7–9.