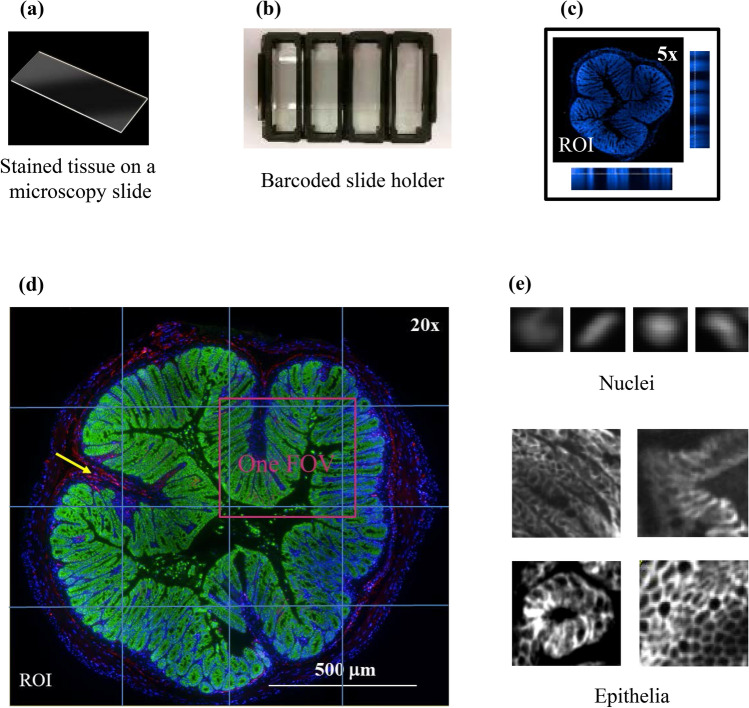
Figure 1.
Automated tissue image acquisition using HCS. (a) A whole frozen colon tissue slice from a αCDH-A647 treated animal was mounted to a standard microscope slide and stained with anti-EpCAM and DAPI. (b) A slide holder with standard microtiter plate footprint was built to house 4 tissue slides in order to facilitate automated image acquisition using the PHENIX HCS reader. (c) A 5 × air objective lens was applied to localize all nuclei (blue), thus defining ROI and providing an optimal Z height starting point. Side images are orthogonal views of maximum nuclear intensity at different Z heights. (d) Automated multi-color (blue: nucleus; green: EpCAM; red: αCDH-A647) rescan on ROI guided by PRECISCAN was conducted using a 20 × water-immersion objective lens. Images from all FOVs were then montaged for analysis. Yellow arrow points to one example of an area where αCDH-A647 was trapped in the interstitial space. (e) Different features of nuclei (top) and epithelia (bottom).