Fig. 1.
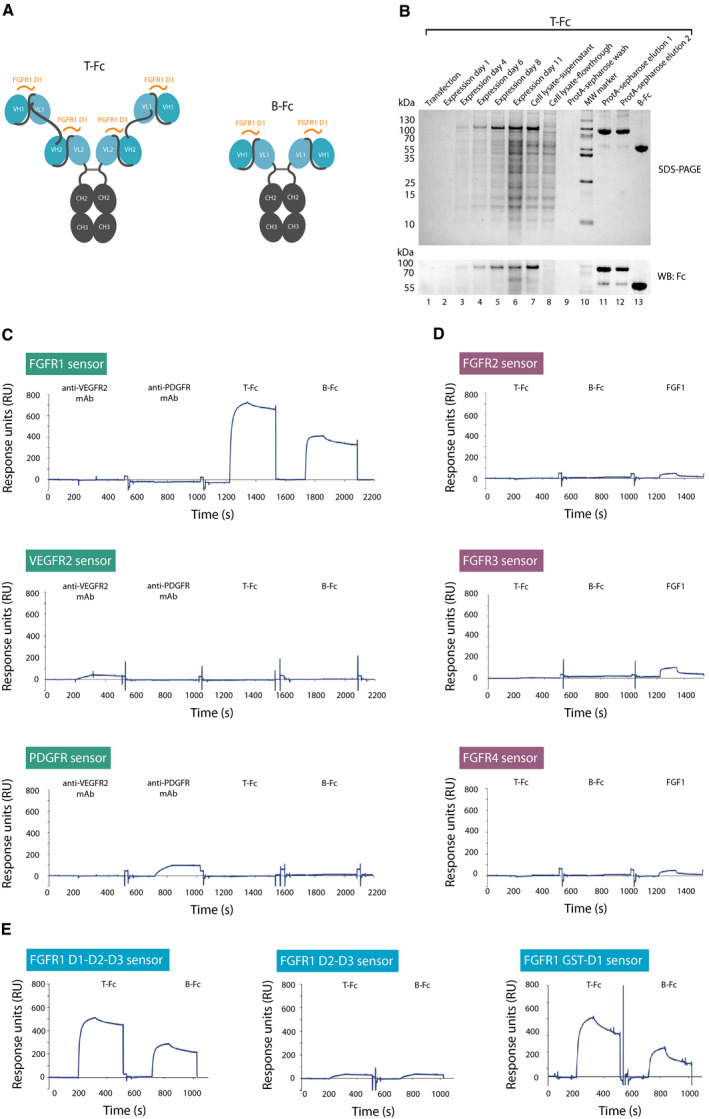
Characterization of anti‐FGFR1 engineered antibodies of different valency. (A) The schematic representation of structures of tetravalent (T‐Fc) and bivalent (B‐Fc) anti‐FGFR1 engineered antibodies. Fc region of IgG (CH2 and CH3 domains) is labeled in gray, and scFv proteins (VH and VL fusions) are marked in blue. Antibody regions recognizing epitopes within FGFR1 are marked in orange. (B) Expression and purification of T‐Fc and B‐Fc. Levels and purity of T‐Fc at different stages of protein expression and purification process were monitored with SDS/PAGE and western blotting with antibodies recognizing Fc fragment. (C) B‐Fc and T‐Fc are specific toward FGFR1. The extracellular regions of FGFR1, VEGFR2, and PDGFR were immobilized on SPR sensors and tested for the interaction with B‐Fc, T‐Fc, and commercial anti‐VEGFR2 and anti‐PDGFR antibodies with SPR. (D) Selectivity tests of B‐Fc and T‐Fc against FGFRs. The extracellular regions of FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4 were immobilized on SPR sensors and tested for the interaction with B‐Fc, T‐Fc, and FGF1 as a control using SPR. (E) Engineered antibodies bind the D1 domain of the receptor. The full‐length extracellular domain of FGFR1 (D1‐D2‐D3), FGFR1 variant lacking the D1 domain (FGFR1 D2‐D3), and recombinant D1 domain (FGFR1 GST‐D1) were immobilized on SPR sensors and tested for interaction with B‐Fc and T‐Fc using SPR.
