Fig. 3.
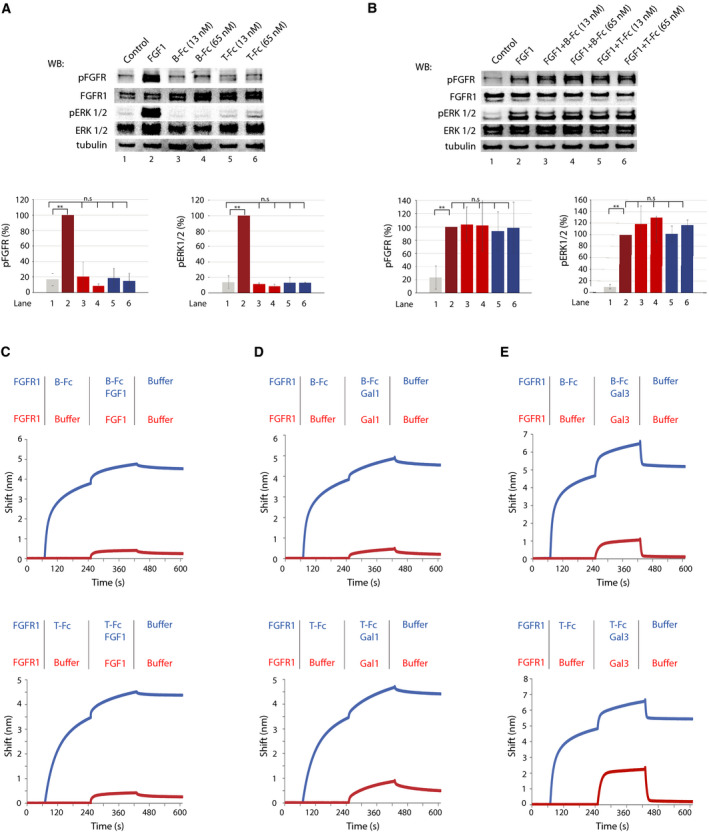
The impact of engineered antibodies on the interaction of FGFR1 with partner proteins. (A) B‐Fc and T‐Fc are unable to activate FGFR1. Serum‐starved NIH3T3 cells were incubated with FGF1 (positive control) or with different concentrations of B‐Fc and T‐Fc. Cells were lysed and activation of FGFR1, and receptor‐downstream signaling was assessed with western blotting (WB). The level of tubulin served as a loading control. Bottom panels: quantification of signaling experiments performed with image lab software. Average values ±SD from at least three independent experiments are shown. The statistical significance was calculated using the t‐test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, n.s.—not significant. (B) B‐Fc and T‐Fc have no impact on FGFR1 activation by FGF1. Serum‐starved NIH3T3 cells were incubated with FGF1 alone or in combination with B‐Fc and T‐Fc. Cells were lysed and activation of FGFR1, and receptor‐downstream signaling was assessed with western blotting. The level of tubulin served as a loading control. Bottom panels: quantification of signaling experiments performed with image lab software. Average values ±SD from at least three independent experiments are shown. The statistical significance was calculated using the t‐test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, n.s.—not significant. (C) The effect of engineered antibodies on FGF1/FGFR1 interaction. The extracellular domain of FGFR1 was immobilized on BLI sensors and either left untreated or incubated with the saturating concentrations of B‐Fc (left graph) or T‐Fc (right graph). Subsequently, sensors were incubated with FGF1 to assess the impact of antibodies on FGF1/FGFR1 interaction. (D) B‐Fc and T‐Fc have no impact on galectin‐1/FGFR1 interaction. The extracellular domain of FGFR1 was immobilized on BLI sensors and either left untreated or incubated with the saturating concentrations of B‐Fc (left graph) or T‐Fc (right graph). Subsequently, sensors were incubated with galectin‐1 to assess the impact of antibodies on galectin‐1/FGFR1 interaction. (E) T‐Fc partially inhibits binding of galectin‐3 to FGFR1. The extracellular domain of FGFR1 was immobilized on BLI sensors and either left untreated or incubated with the saturating concentrations of B‐Fc (left graph) or T‐Fc (right graph). Subsequently, sensors were incubated with galectin‐3 to assess the impact of antibodies on galectin‐3/FGFR1 interaction.
