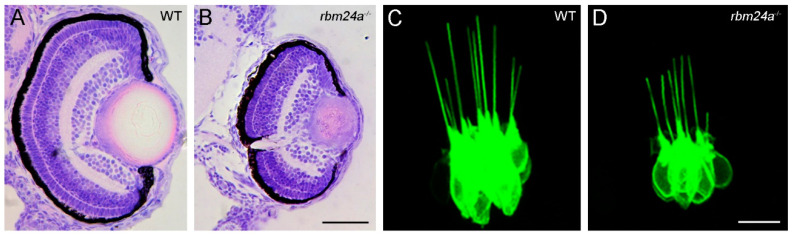
Figure 4.
Loss of Rbm24a function impairs lens transparency and affects inner ear hair cell development in zebrafish. (A,B) Histological sections of ocular tissues at the level of the optic nerve compares lens differentiation between a wild-type (WT) sibling (A) and an rbm24a mutant (B) at 3 dpf (days post-fertilization). The sections were stained by hematoxylin and eosin. Loss of Rbm24a disrupts lens differentiation and causes cataract formation, but has no effect on retina differentiation. The microphthalmia phenotype and defective lens fiber cell denucleation are secondary consequences due to impaired blood circulation [20]. (C,D) Confocal microscopic analyses compare hair cell development and organization in the lateral crista of the zebrafish inner ear from a wild-type (WT) sibling (C) and an rbm24a mutant (D) at 3 dpf, under the Tg(pou4f3:GAP-GFP) transgenic background [40]. Scale bars: (A,B), 50 µm; (C,D) and 10 µm.