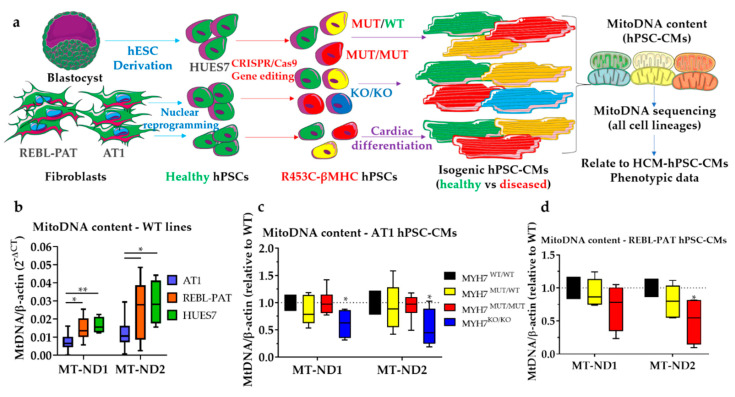
Figure 1.
Harnessing isogenic hPSC-CM models to investigate varying HCM mitochondrial phenotypes. (a) Study workflow: hPSC were generated from three different healthy cell sources, followed by the introduction of the p.R453C-βMHC mutation by CRISPR/Cas9. Isogenic healthy and diseased (heterozygote or homozygote) mutant hPSCs were differentiated into cardiomyocytes and mtDNA content and sequence was evaluated. (b) Ratiometric qPCR analysis of mitochondrial: nuclear DNA highlighted variations in mitochondrial content across healthy (WT) lines, with AT1 lines showing 50–60% lower mtDNA content relative to HUES7 and REBL-PAT hPSC-CMs. Isogenic (c) AT1 and (d) REBL-PAT hPSC-CMs did not display striking changes in mtDNA content, with the exception of the AT1 MYH7-knockout line. Data are presented as box and whiskers plots, n = 5–8 biological replicates, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test in (b) and one-way ANOVA + Dunnett’s correction relative to WT in (c,d)).