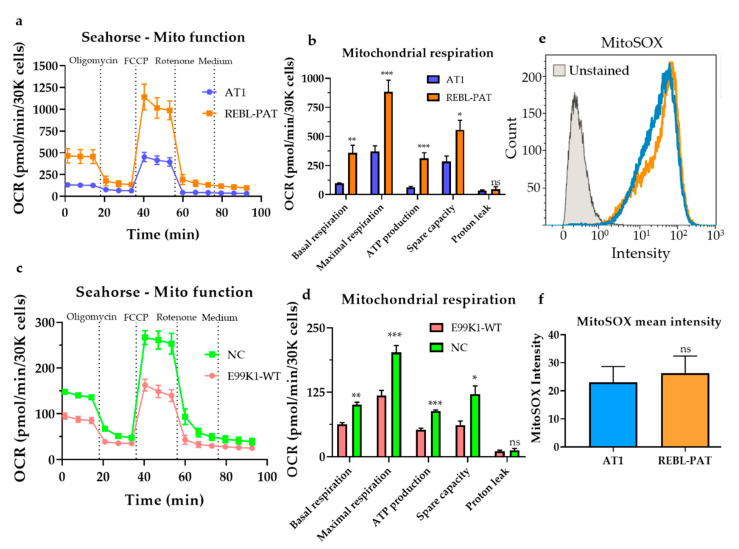
Figure 4.
Mito-modulating effects of mtDNA variants identified in hPSC-CMs. (a) Mitochondrial respiration was evaluated by Seahorse analysis of healthy hPSC-CM lines used to model the p.R453C-βMHC sarcomeric mutation, showing (b) higher oxidative phosphorylation activity in REBL-PAT cardiomyocytes relative to the AT1 line, presenting different mtDNA variants. (c,d) The healthy (gene-corrected) E99K1-WT hPSC-CM line showed lower mitochondrial respiration activity relative to NC hPSC-CMs displaying diverse mtDNA variants. (e,f) Evaluation of mitochondrial ROS production by flow cytometry of MitoSOX-labelled hPSC-CMs showed no difference between healthy AT1 vs REBL-PAT hPSC-CMs, indicating that the mtDNA variants identified in these lines do not contribute to mito-dysfunction. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, N = 5-7 biological replicates, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, n.s., non-significant (Student’s t-test); OCR, oxygen consumption rate.