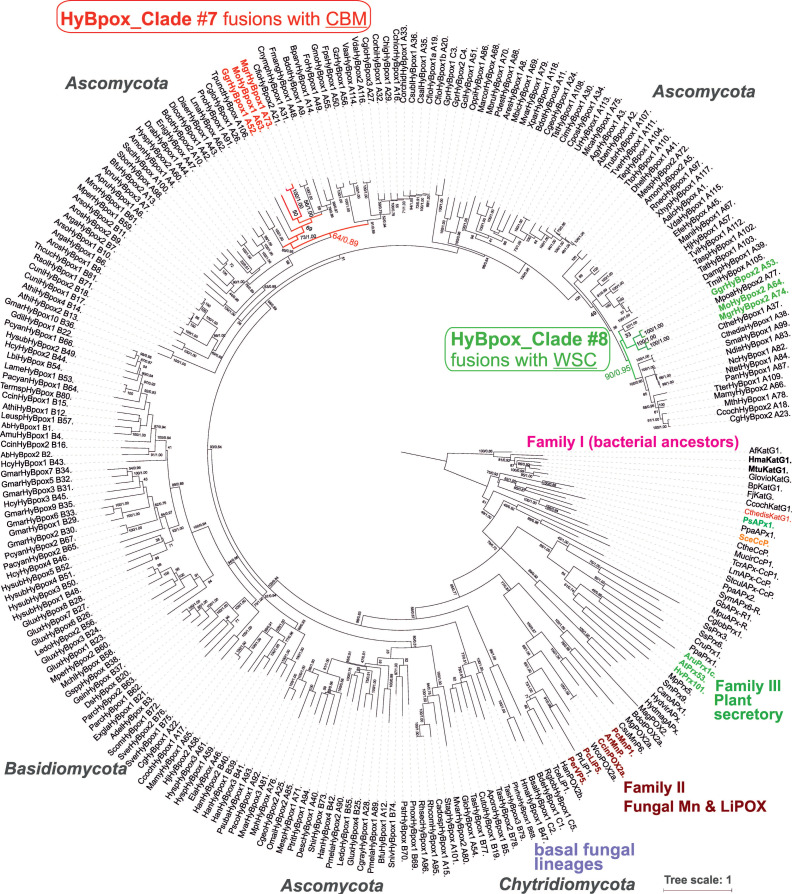
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic position of sequences coding for peroxidases from phytopathogenic representatives of the fungal family Magnaporthaceae analysed in an unrooted phylogenetic tree for all known hybrid B peroxidase sequences and selected representatives from all other known clades of the peroxidase-catalase superfamily. Presented is a tree topology obtained with the maximum likelihood method of the MEGA X package [21]. Whelan and Goldman (WAG) as the best substitution model for this dataset of 250 complete protein sequences was used with 5 gamma categories and invariant sites and 100 bootstrap replicates. A very similar tree topology was obtained also with the Mr Bayes approach [22] with a relative burn-in of 25% performed over 1,500,000 generations. Numbers in the nodes represent bootstrap values and posterior probabilities, respectively (presented are only values above 33/0.5). All here used abbreviations of peroxidases correspond with RedoxiBase [1] (http://peroxibase.toulouse.inra.fr/).