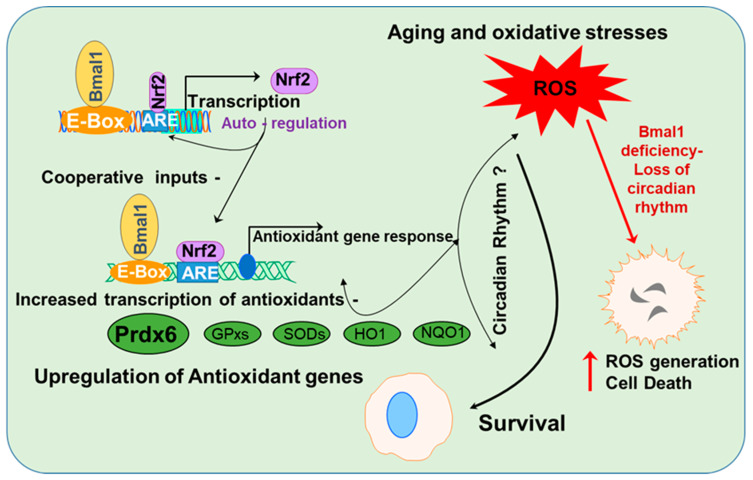
Figure 10.
Illustration of proposed model for Bmal1 and Nrf2-mediated cellular protection against environmental stresses or aging. We observed that the biological clock gene, Bmal1 is crucial in promoting the antioxidant gene transcription in mouse lens/hLECs. Here we show plausible direct and indirect mechanism in which Bmal1 may defend the lenses/LECs by regulating antioxidant genes. In direct mechanism, Bmal1 directly regulates the antioxidant genes like Prdx6 transcription by binding to its E-Box elements. In indirect mechanism of regulation, Bmal1 regulates the expression of Nrf2 through E-Box elements present in the promoter region. Then Nrf2 activates antioxidant defense by binding to the ARE sequence present in the promoter region of the target antioxidants, here Prdx6. Our work revealed that both Bmal1 and Nrf2 regulate Prdx6 transcription; we proposed that cooperativity of Bmal1 and Nrf2 is an important phenomenon for peaking Prdx6 expression and cellular protection. Additionally, our findings reveal that molecular clock controls the Nrf2 and its antioxidant targets, like Prdx6 expression levels, to defend lens/hLECs by controlling ROS homeostasis.