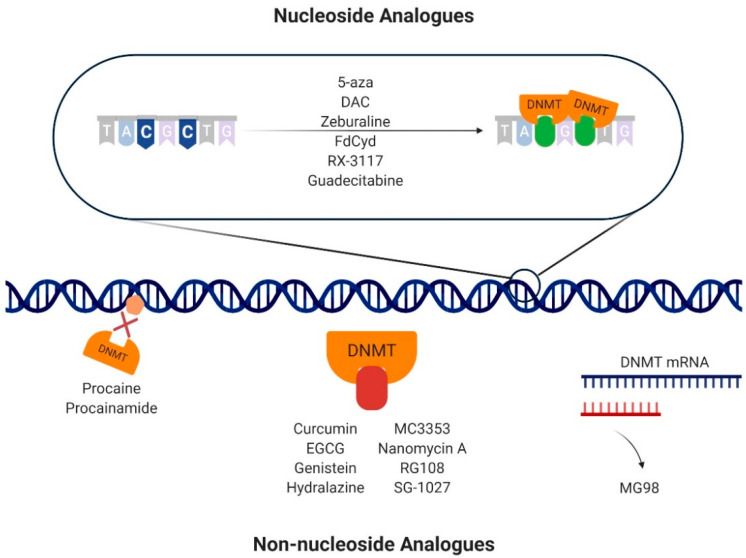
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of action of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) inhibitors. The nucleoside analogues 5-azacitydine (5-aza), decitabine (DAC), zebularine, 5′-fluoro-2′-deoxycytidine (FdCyd), RX-3117, and guadecitabine are integrated into DNA instead of cytosine. When DNMTs bind, a covalent bond is formed between the DNMT and the cytosine analogue. The non-nucleoside analogues have different mechanism of action to achieve inhibition of DNA methylation. Specifically, procaine and procainamide bind directly to the DNA, impeding DNMT binding. Curcumin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), genistein, hydralazine, MC3353, nanomycin A, RG108, and SG-1027 bind directly to the catalytic pockets of DNMTs, hampering their action. MG98 is an oligodeoxynucleotide that binds to the DNMT1 messenger RNA (mRNA) by base pair complementarity, impeding its translation.