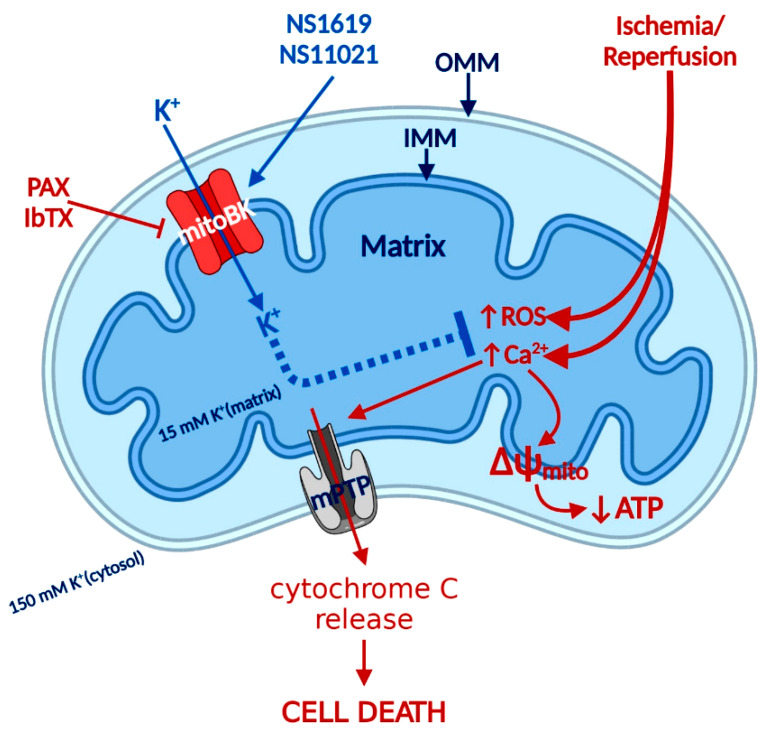
Figure 1.
BKCa signaling in cardiomyocytes mitochondria during ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. I/R injury causes an increase of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and Ca2+ overload that leads to mPTP opening, the collapse of membrane potential (ΔΨIMM), and the release of cytochrome C that causes cell death. The opening of BKCa protects the heart by reducing ROS and increasing the calcium retention capacity, hence delaying the opening of mPTP. IMM—Inner mitochondria membrane, OMM—Outer mitochondria membrane. mitoBKCa activators (NS1619, NS11021), mitoBKCa inhibitors (PAX-paxilline, IbTX-iberiotoxin), mPTP-mitochondrial permeability transition pore.