Figure 7.
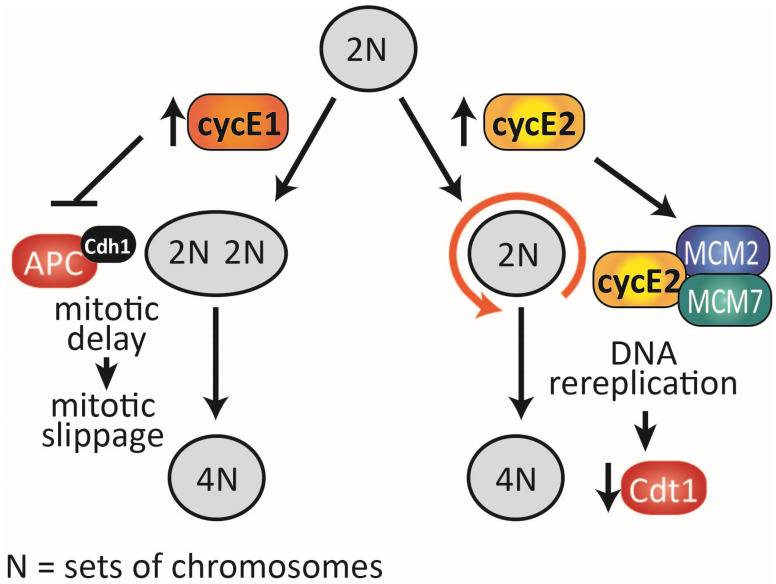
Cyclins E1 and E2 are associated with genome doubling, but through different mechanisms. Excess cyclin E1 blocks the action of the APC (Cdh1) complex [13,19], leading to delayed mitosis through a delay in the degradation of cyclin B1. A common consequence is mitotic slippage, resulting in a 4N state. Excess cyclin E2 is not associated with mitotic slippage. Instead, cyclin E2 has enhanced binding to the MCM2 and MCM7 proteins of the pre-replication complex that initiates DNA replication, and excess cyclin E2 leads to DNA rereplication. Rereplicated cells enter a 4N state, and cells downregulate Cdt1 as part of a negative feedback loop to prevent further rereplication. N = sets of chromosomes.