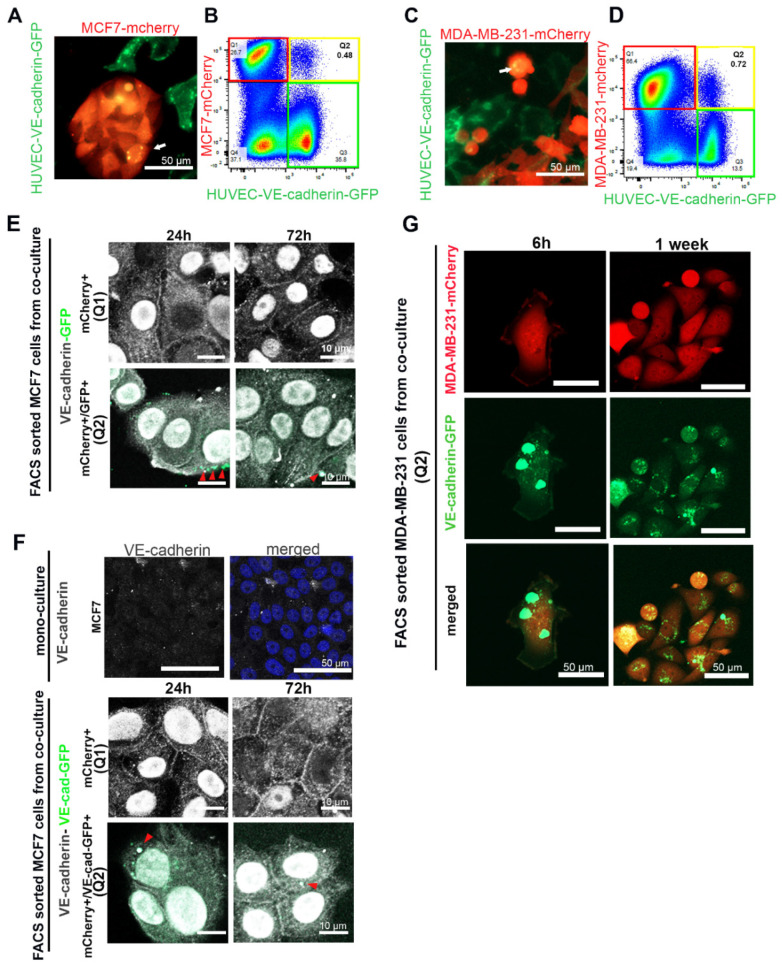
Figure 5.
Cancer cells took up VE-cadherin from HUVECs. (A) MCF7-mCherry or (C) MDA-MB-231-mCherry were co-cultured with HUVECs expressing VE-cadherin-GFP. The arrows show VE-cadherin-GFP-containing vesicles that were taken up in breast cancer cells. (B) MCF7-mCherry or (D) MDA-MB-231-mCherry co-cultured with HUVEC-VE-cadherin-GFP for 72 h were analyzed by flow cytometry. Red frames denote the mCherry-positive cell population Q1 (MCF7 or MDA-MB-231 cells), green frames indicate VE-cadherin-GFP-expressing HUVECs, and yellow frames highlight the population Q2 of mCherry+/GFP+ double-positive cells. (E,F) After MCF7-mCherry cells were co-cultured for 3 days with (E) HUVECs-GFP or (F) HUVECs-VE-cadherin-GFP, we isolated mCherry+ single-positive cells (Q1) and mCherry+/GFP+ double-positive cells (Q2) and stained them with an antibody against VE-cadherin (C-19) (shown in gray). VE-cadherin localized at cell–cell junctions and in the nucleus of isolated cells. Arrows indicate GFP-positive (E) or VE-cadherin-GFP containing (F) EC-derived membrane vesicles taken up by MCF7-mCherry+/GFP+ cells. These vesicles were also positively stained for VE-cadherin by immunofluorescence staining (gray intensity). MCF7 cell monoculture was used as a negative control for VE-cadherin staining. (G) After having been co-cultured with VE-cadherin-GFP-expressing HUVECs for 72 h, MDA-MB-231-mCherry cells were isolated with FACS and cultured for 1 week in the absence of HUVECs. Even 1 week after isolation, VE-cadherin-GFP vesicles could be detected in the MDA-MB-231 cells.